Circadian rhythm is your body’s internal clock that permits anticipation of daily patterns. This study evaluated the effects of NR supplementation on age-related changes in the heart’s circadian rhythm.
Key Points
- NR Boosted NAD+ levels
- Age-induced heart enlargement was prevented
- NR modulated age-associated changes in the heart’s circadian genes
Animal Study Evaluates Effects of NR on Cardiac Circadian Rhythm
Female mice were divided into groups (n= 3-4/ group):
- Young: 2 months old; received standard diet and water
- Old, H2O: 12 months old; received standard diet and water
- Old, NR: 12 months old; received standard diet and water + NR (3 g/L)
NAD+ Levels were Boosted
NR supplementation significantly increased NAD+ levels in the liver, while modest increases were observed in the heart.
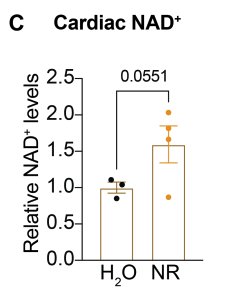
This figure shows a modest increase in cardiac NAD+ levels in mice supplemented with NR (yellow dots) relative to mice that received standard water (black dots).
Age-Associated Heart Enlargement was Prevented
“We observed that naturally occurring cardiac enlargement was completely abolished in NR-treated mice.”
The figure below shows untreated, old mice (yellow bar, black dots) had significantly larger hearts compared to young mice (black bar, black dots). When supplemented with NR, the old mice did not experience heart enlargement (yellow bar, yellow dots).
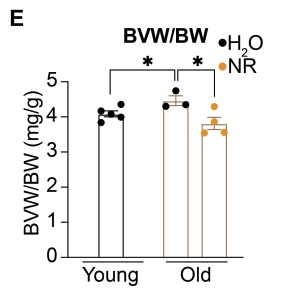
“Showing that the supplementation strategy does positively affect the heart.”
Modulated Circadian Gene Expression in the Heart
The researchers measured gene expression at night and during the day to evaluate the effects of NR on the heart’s circadian rhythm.
Many differences in cardiac gene expression were found between young and old mice. However, the data showed NR had positive effects:
- Maintained a youthful rhythm in 110 genes
- Prevented 111 genes from developing age-related irregularities
Conclusion
This study showed that NR supplementation modulated cardiac gene expression in aged mice to promote a more youthful circadian rhythm.
“These findings reveal an essential role for NAD+ in regulation of the cardiac circadian clock upon aging”
