Body Protection Compound-157 (BPC-157) is a peptide recognized for its regenerative and healing properties.
Derived from a protein naturally found in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, BPC-157 has been extensively studied for its ability to protect cells, stimulate new blood vessel formation, and reduce inflammation – all essential processes for tissue repair and recovery.
Its potential to accelerate tissue regeneration has made it a promising candidate for addressing joint pain, mobility issues, and injury recovery.
Key Points
Animal studies suggest that BPC-157 offers widespread healing benefits across the body, including:
- Accelerated healing and functional recovery of tendons, ligaments, muscles, and bones
- Support for wound healing through key regenerative processes
- Reversal of corticosteroid-induced damage
- Protection and therapeutic effects on gut health, including inflammatory conditions and ulcers
- Nerve regeneration and neuroprotection against spinal cord injury, brain trauma, and neurotoxicity
- Improvements in motor function, learning, mood regulation, and neurodegenerative conditions

Tendon, Ligament, and Muscle Repair
BPC-157 has accelerated the healing of various tissues, including tendons, ligaments, muscles, and bone in numerous preclinical studies.
- Achilles Tendon: Improved recovery, strength, collagen formation, and reduced inflammation in mice with torn Achilles tendon (1)
- Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL): Sped up healing equally across oral, topical, and injectable administration (2)
- Tendon-to-Bone Repair: Promoted healing even with corticosteroid use, which typically impairs recovery (3)
- Muscle Regeneration: Accelerated repair and restored function in quadriceps and crushed muscle injuries (4, 5, 6)
- Bone Fractures: Enhanced bone regeneration, likely by stimulating angiogenesis and reducing inflammation (7)
Wound Healing
BPC-157 speed up wound healing in animal models by improving key processes:
- Building New Tissue: Enhances granulation tissue formation (the early stage of healing) and collagen production (the protein that gives structure to tissues)
- Controlling Inflammation: Controls excessive inflammation, preventing delayed healing
- Growing New Blood Vessels: Supports new blood vessel growth, ensuring oxygen and nutrient delivery
“The combined triad of collagen-inflammatory cells–angiogenesis was accordingly upgraded, appearing at earlier intervals, more rapid, and advanced with BPC 157 therapy.” (8)
These improvements have been seen in various types of wounds, suggesting BPC-157 may have a broad healing effect. (9)
“The noted wide effectiveness in all of these models postulates a quite general wound healing effect” (8)
BPC-157 reduced inflammation and tissue death, and promoted skin regrowth in mice with severe burns. (10)
It outperformed the standard burn treatment, silver sulfadiazine, in some studies. (10)
Gut Health and Healing
Research in model organismss indicates that BPC-157 may support gut health by:
- Strengthening the Gut Lining: Enhances the mucosal integrity, which is the protective layer of the stomach and intestines
- Reducing Inflammation: Helps calm gut irritation and inflammatory conditions
- Promoting Tissue Repair: Accelerates the healing of damaged tissue in the gut
- Protecting Blood Vessels: Supports healthy blood vessel function, improving circulation to injured areas
These effects have been observed in several conditions:
- Gastric Ulcers: Accelerates healing, outperforms some ulcer medications, and promotes tissue regeneration (11)
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Enhances mucosal integrity, reduces inflammation, and supports epithelial repair (12)
- Gut Surgery: Improves healing of intestinal connections (anastomoses) and abnormal gut fistulas (13, 14)
- Overall Gut Health: Supports blood vessel formation, protects the gut lining, and may help with IBS symptoms (12)
- Damage Protection: Shields against alcohol, NSAIDs, and toxins while aiding healing in the esophagus, liver, and pancreas (13)
Neurological Protection and the Gut-Brain Axis
Animal studies have demonstrated that BPC-157 has broad neuroprotective and therapeutic effects, including:
- Neuroprotection and Recovery: Supports nerve regeneration, protects against spinal cord injury, brain trauma, and neurotoxicity (14, 15)
- Neurotransmitter Regulation: Modulates dopamine, serotonin, and GABA, influencing seizures, tremors, addiction, and neurological disorders (16)
- Behavioral and Cognitive Support: Improves motor function, learning, mood disorders, and neurological decline (16)
By promoting both gut healing and neuroprotection, BPC-157 is a promising therapy for conditions linked to the gut-brain axis, supporting systemic healing and recovery.
“It is conceivable for realization of the brain-but axis and for stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 that its strong beneficial background on the periphery implies a corresponding beneficial central influence.” (17)
Human Studies
While most BPC-157 research consists of animal studies and anecdotal reports, a few small-scale human studies have explored its potential therapeutic effects.
- Interstitial cystitis: In a trial of 12 women (ages 39-76) with moderate to severe interstitial cystitis unresponsive to conventional treatment, a single 10 mg BPC-157 injection led to complete symptom resolution in 10 patients and 80% improvement in 2, with no reported adverse effects (18)
- Knee pain: A retrospective study found that 11 of the 12 patients (91.6%) receiving BPC 157 as an intra-articular injection had significant improvement in knee pain, whereas 1 patient (8.3 %) had no improvement (19)
Efficacy of BPC 157 Delivery Methods
BPC-157 can be administered orally, topically, or via injection.
While oral peptides typically have limited systemic effects, studies suggest orally ingested BPC-157 may still impact tissues beyond the gut. (20)
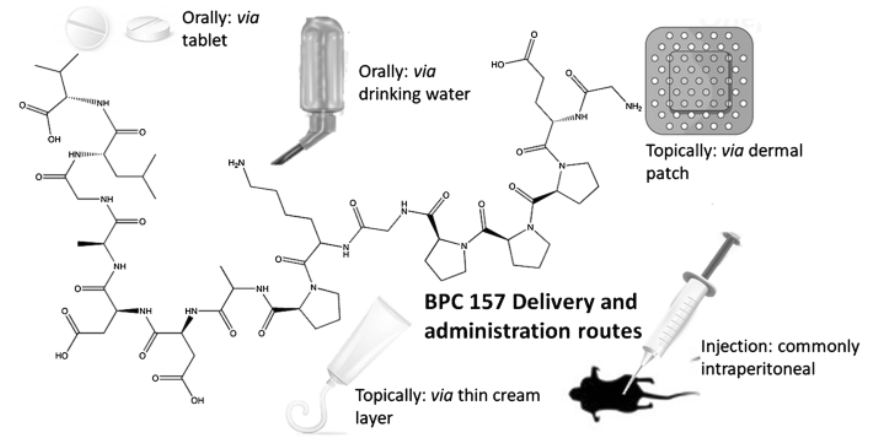
This figure illustrates the mechanisms that can be used to effectively administer BPC-157. (21)
It is highly stable, remaining intact in gastric juice for over 24 hours, and has a strong safety profile (no lethal dose identified).
Conclusion
BPC-157 shows broad regenerative potential, accelerating tissue repair, reducing inflammation, and promoting th growth of new blood vessels across musculoskeletal, gastrointestinal, and neurological systems.
Its unique role in the brain-gut axis supports both gut health and neuroprotection, influencing neurotransmitter balance and nerve regeneration, making it relevant for inflammatory disorders, injuries, and neurodegenerative diseases.
With multiple delivery options – including oral, topical, and injectable formulations – alongside high stability and a strong safety profile, BPC-157 shows significant therapeutic potential.
While ongoing research underscores its potential as a breakthrough in regenerative therapy, further human trials are essential to fully elucidate its long-term safety, efficacy, and clinical applications.
