A new NMN human trial using 80 middle-aged healthy adults showed that NMN supplementation was both safe and well tolerated. It also showed that NMN significantly raised NAD+ blood levels, increased endurance, and benefited bioage.
Study set out to determine safety and efficacy of NMN supplementation in 4 groups
NAD+ levels are known to decline with age, affecting longevity and age-related health conditions, better known as the “diseases of old age”. This 60-day trial set out to determine the safety and efficacy of NMN supplementation in 4 different groups.
The study was a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, dose-dependent clinical trial. It divided 80 middle-aged healthy adults into 4 different groups of once daily oral dosing of placebo, 300 mg, 600 mg, or 900 mg of NMN.
The primary objective of the study was to evaluate blood NAD+ concentration levels using various dose-dependent regimens. The secondary objectives were to assess the safety and tolerability of NMN supplementation, along with evaluating clinical efficacy by measuring physical performance in a six-minute walking test and blood biological age.
Endurance improved in six-minute walking tests for NMN groups
The American Thoracic Society has developed guidelines for a six-minute walking test in clinical settings. In healthy subjects, the six-minute walk distance (6MWD) can range from 400 to 700 meters with the main predictor variables being gender, age and height.
The six-minute walking test in this study was conducted by adapting the protocol issued by the American Thoracic Society for measuring endurance and energy levels. It was conducted at days 0, 30, and 60.
During the 6-minute walking test, participants were asked to walk on a manual treadmill, which can mimic a normal outdoor walk. Distance in meters was recorded through a digital odometer on the treadmill. Results showed that endurance was increased in ALL the NMN groups in all days measured.
“Walking distance increase during the six-minute walking test was statistically significantly higher in the 300 mg, 600 mg, and 900 mg groups compared to placebo at both days 30 and 60” (1)
NMN supplementation significantly raised blood NAD+ levels
Each participants’ blood sample was taken at days 0, 30, and 60 at trial centers. The study found that blood NAD+ concentrations were statistically significantly increased among all NMN-treated groups at day 30 and day 60 when compared to the placebo and baseline groups. The study showed highest blood NAD+ concentrations were in the groups taking 600 mg and 900 mg NMN per day.
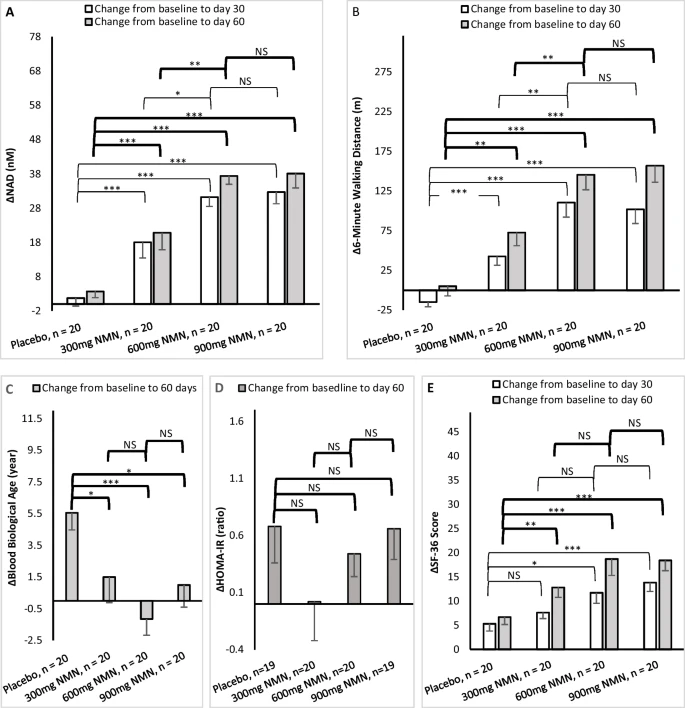
Study shows benefit to biological age in treated groups
A blood bioage test allows you to compare chronological age with biological age. Using this information, someone would be able to take a more proactive approach in reducing their biological age, leading to improved longevity and a longer overall “health-span.”
In the study, the blood biological age increased in the placebo group, which might be expected over time. However, bioage stayed unchanged in all NMN-treated groups at day 60, resulting in a statistically significant difference between the treated and placebo groups.
Patients reported success in measures of health improvement
Assessment of participants’ overall health status or quality of life was determined in a 36-question self-assessment test (called SF-36) at days 0, 30, and 60. The NMN groups all reported they had significantly more positive results in their self-assessment of overall health.
“The change of SF-36 scores at day 30 and day 60 indicated statistically significantly better health of all three treated groups when compared to the placebo group” (1)
References
