In a recent publication, researchers conducted a systematic review of all NMN human trials that were published at that time, to understand its potential anti-aging effects while further validating its safety.
The review covered 12 human trials, but there have been numerous studies published after the review was conducted. We keep a list of all NMN human trials here, with 17 published to date *.
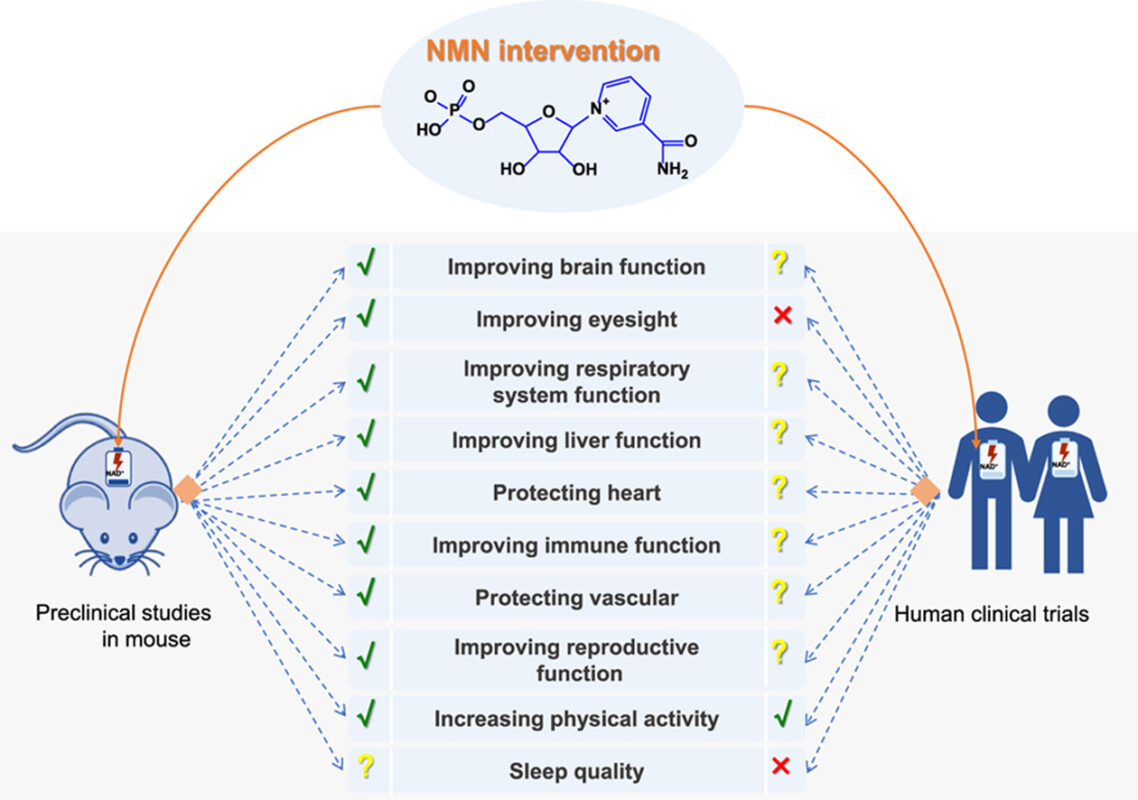
The authors of this review noted that NMN has gained much of its popularity due to the promising findings in cell and animal studies.
According to the paper, “preclinical studies of NMN intervention in mouse models have shown that increasing NAD+ concentration could prevent and treat age-related diseases via improving tissue and organ function, reducing inflammation, enhancing immune and reproductive function, increasing physiological benefits and protecting cognitive function.” But, the human trials in NMN have not matched the success levels of the studies in mice.
It is always difficult to translate success in mouse studies to research in humans due to cost, safety, and limited time for study, however there has been some success in the human NMN studies covered in this review. We note those below.
* One study published after this review stands out as the most successful in humans to date, finding NMN significantly reduced cholesterol, body weight, and diastolic blood pressure.
Image Source: The Safety and Anti-Ageing Effects of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide in Human Clinical Trials: An Update
Key Findings:
- Potential improvements in hearing abilities in a study of older men
- Telomere lengthening was shown in a small study of middle-aged men
- Muscle strength, performance, and walking speed improvements in a study of older adults
- Improvements of insulin sensitivity and signaling in muscles, in a study of overweight older women with pre-diabetes
- IP injection was shown to be much more effective than orally administered NMN
- Some NMN is taken up directly by cells without breakdown to NAM, NR, or NA
* Last 2 points were derived from studies in mice, not humans
NMN Prevented Telomere Shortening, a Hallmark of Aging
Telomeres are protective caps at the ends of your chromosomes that protect your DNA and are known to shorten with age.
The effect of NMN supplementation on telomere length was examined in a study with eight middle-aged men (aged 45–60 years).
“They discovered that NMN supplementation resulted in a nearly doubled telomere length in PBMCs within 90 days, indicating a potential anti-ageing effect.”
NMN Improved Muscle Strength & Performance
One study found that NMN supplementation enhanced muscle strength and performance, and improved walking speed in older men.
“Kim et al. evaluated the effect of oral NMN on physical performance in older individuals, including grip strength, 5-times sit-to-stand (5-STS), timed up and go and a 5-m habitual walk.”
Walking Endurance & Aerobic Capacity Improved
Researchers also tested older individuals (ages 40-65) in a study using a 6-minute walking endurance test after NMN intervention. The NMN group showed sustained improvement in walking endurance from 30 to 60 days of treatment.
- This study found that NMN supplementation increased oxygen and energy consumption, which led to enhanced aerobic capacity in middle-aged recreationally trained runners.
“These results indicate that physical training combined with oral NMN administration could be a new strategy to improve athletes’ performance.”
NMN Improved Insulin Signaling in Pre-Diabetes
A clinical trial found that NMN supplementation for 10 weeks improved insulin sensitivity and insulin signaling in the muscle of overweight or obese postmenopausal women with prediabetes.
“Surprisingly, after NMN intervention, participants’ insulin sensitivity was improved by 25±7%”
NMN and Resveratrol Combined, Increased Tissue Levels of NAD+
A study in mice aimed to better understand how effective NMN could be at raising tissue NAD+ levels, when combined with other supplements.
The study showed that NMN combined with resveratrol raised heart and muscle NAD+ significantly.
“Compared with NMN alone, NMN combined with resveratrol could increase the levels of NAD+ in the heart and muscle by about 1.6 times and 1.7 times.”

NMN is Found to be Safe in Numerous Trials
Several human clinical trials have been conducted to assess the safety and efficacy of NMN supplementation. (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8)
The results of these trials suggest that NMN is safe and well-tolerated up to a dosage of 1000 mg twice a day for two weeks. (9)
“The findings of these studies suggest that the administration of NMN orally is safe and has good tolerance.”
Ongoing Clinical Trials
There are numerous clinical trials underway assessing the effects on NMN supplementation in humans.
Specific objectives of the current clinical trials aim to better understand:
- The safety and metabolism of NMN supplementation in healthy adults (ages 18-70)
- The effects of NMN supplementation on various diseases, including diabetes, chronic disease, hypertension, polycystic ovary syndrome, and premature ovarian failure
- The anti-aging effects of NMN supplementation on the skin
- Study changes in various hormonal levels and aging markers, male fertility indicators, cardiovascular and metabolic functions, and physical activity
- The impact of NMN compared to other NAD+ precursors on blood NAD+ levels
Oral Delivery Is Not As Effective as Injections
This study evaluated the pathways involved in the conversion of NMN to NAD+ in mice, in an effort to understand how these mechanisms may work in humans. Although not a human study, the results were significant because it shows that the delivery method can greatly impact absoprtion and effectiveness.
The study compared intraperitoneal (IP) injection and oral administration of NMN. The results clearly demonstrated that oral delivery of NMN in mice is not as effective as injections.
“IP injection of 500 mg/kg NMN resulted in a significant increase in blood nicotinamide levels, reaching over 16-fold at 2 h post-treatment.”
The IP injection of NMN resulted in a significant increase in NAD+ levels.
“The administration of NMN through IP injection allowed for rapid delivery and a strong enhancement of NAD+ levels, while oral gavage results in a slower delivery with less impact on NAD+ metabolism.”
Some NMN Was Taken Up Directly By Cells
The study demonstrated that some IP-injected NMN was taken up directly by cells, without breaking down to NAM, NR or NA.
“We also found a small amount of direct incorporation of intact NMN in the kidney and epidydimal white adipose, suggesting that NMN can be transported into these organs via a transporter and converted to NAD+.”
“We, therefore, conclude that the transport of intact NMN likely occurs in small quantities in the kidney and white adipose tissues.”
Updated List of All Human NMN Trials
Since the publication of this review, the results of several clinical trials on NMN have been published. A complete list of these trials can be found here. Studies 9,10, 12-17 were not reviewed in this publication.