This study examined the effects of Apigenin on inflammation, gut barrier integrity, and the gut microbiome in mice with ulcerative colitis (UC).
Key Points:
Apigenin benefited mice with ulcerative colitis (UC) in several ways:
- Reduced the severity of UC
- Restored the gut inflammatory balance
- Strengthened the gut barrier
- Remodeled the gut microbiome
- Boosted the production of short-chain fatty acids
Study Investigates the Effects of Apigenen in Mice with Experimentally-Induced Ulcerative Colitis
Mice were randomly divided into five groups (n = 6 per group):
- Control group: healthy and did not receive treatment
- Model group: had UC and did not receive treatment
- Positive medicine group (SASP): had UC and received a medicine used to treat UC (SASP)
- Low-dose apigenin (AP-L) group: had UC and received 150 mg/kg of apigenin
- High-dose apigenin (AP-H) group: had UC and received 250 mg/kg of apigenin
The experimental mice were given dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) in their drinking water for 23 days to induce UC. After 2 days, the mice in the treatment groups began their regimen by orally receiving their treatment once a day for 21 days.
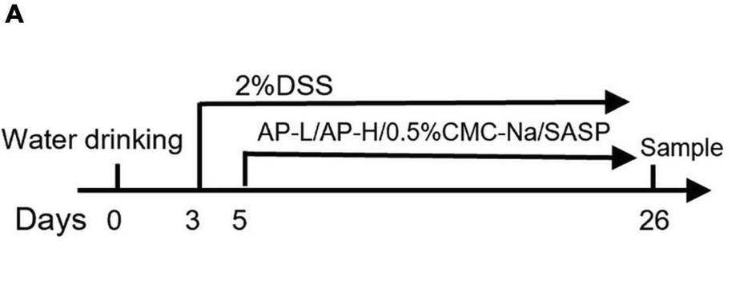
Experimental design: Ulcerative Colitis (UC) was induced in mice on day 3 by the administration of 2% DSS in their drinking water. On day 5, the mice in the positive medicine group, low-dose Apigenin group, and high-dose Apigenin group began receiving their respective treatments. The experiment lasted 26 days.
The Severity of Ulcerative Colitis was Reduced
The researchers assessed UC severity in mice using a Disease Activity Index (DAI) score, which considers fecal consistency, fecal occult blood, and weight loss.
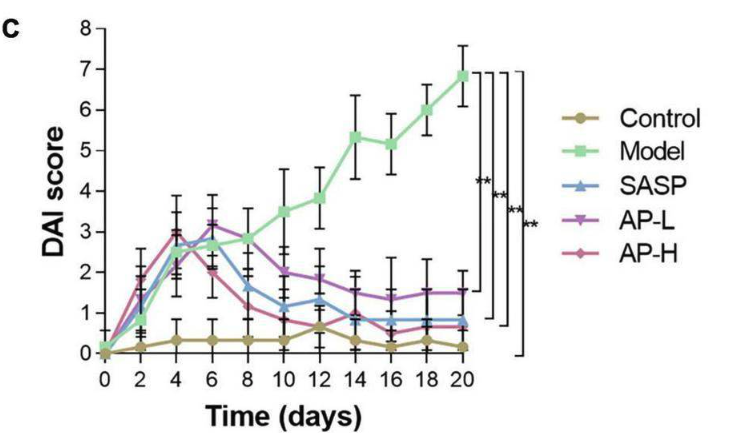
The induction of UC increased DAI scores in untreated mice (green line). Mice with UC given Apigenin at low (purple line) or high doses (pink line) had lower DAI scores, similar to UC mice receiving medicine (blue line) and those without UC (yellow line).
Both low and high doses of Apigenin also prevented weight loss and spleen enlargement in mice with UC, as observed in untreated UC mice.
“Overall, these results indicated that apigenin administration treatment significantly ameliorated DSS-induced UC.”
Inflammatory Balance in the Gut was Restored
Apigenin treatment decreased the levels of the pro-inflammatory molecules TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, and increased the levels of the anti-inflammatory molecule, IL-10, in the colons of the UC mice.
This figure represents the levels of TNF-α, a pro-inflammatory molecule, in the colons of the mice.
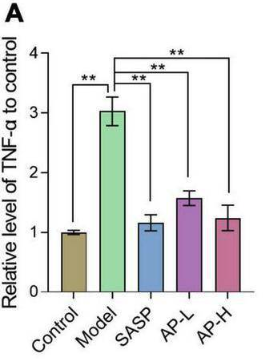
Untreated mice with UC (green bar) had significantly elevated levels of TNF-α compared to healthy mice (yellow bar). Mice with UC treated with low- (purple bar) or high-dose (pink bar) Apigenin had significantly lower levels of TNF-α compared to untreated mice.
The mice receiving Apigenin also had reduced levels of myeloperoxidase (MPO), a marker of inflammation, compared to untreated mice with UC.
“These results suggested that apigenin alleviated inflammation and kept intestinal homeostasis.”
The Gut Barrier was Strengthened
The researchers evaluated gut barrier integrity by measuring three tight junction proteins in the mice’s colons: ZO-1, claudin-1, and occludin.
Tight junction proteins maintain cell-to-cell barriers, which is crucial for gut barrier integrity.
The levels of Occludin, a tight junction protein, in gut tissue are depicted in the figure below.
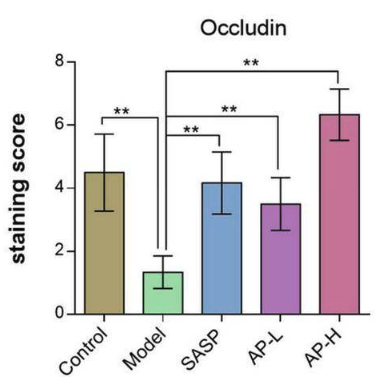
Occludin levels decreased in mice with UC (green bar), signifying a more permeable gut barrier. However, UC mice given low-dose (purple bar) or high-dose (pink bar) Apigenin maintained occludin levels akin to healthy mice (yellow bar).
Notably, mice with UC receiving high-dose Apigenin (pink bar) exhibited higher occludin levels than those receiving medication (blue bar).
“However, SASP and apigenin might improve this change, and high-dose apigenin might have a better effect compared with SASP.”
The Balance of Gut Bacteria was Improved
Apigenin increased levels of beneficial gut bacteria, protecting the gut barrier, and reduced levels of harmful bacteria that are linked to UC.
“In the top 35 genus level, 16 genera were downregulated and 12 genera were upregulated in the DSS-induced mice, while SASP and apigenin supplementation selectivity reversed this change.”
For example, an abnormal abundance of Proteobacteria was observed in untreated UC mice and was reversed by Apigenin.
“Through 16S rRNA gene sequencing, we found that the reduction of Proteobacteria was observed by the apigenin and SASP intervention, which indicated that apigenin supplementation may regulate intestinal microbial composition and richness to rebalance gut microbiome.”
Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids was Boosted
Treatment with Apigenin increased the levels of short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) in the gut, which are nutrients produced by the microbiome that have anti-inflammatory and protective effects on the gut barrier.
“But apigenin and SASP administration significantly increased the level of SCFAs, and the SCFA content of AP groups was almost as effective as positive drugs.”
Protective Effects of Apigenin Against UC observed in the Study
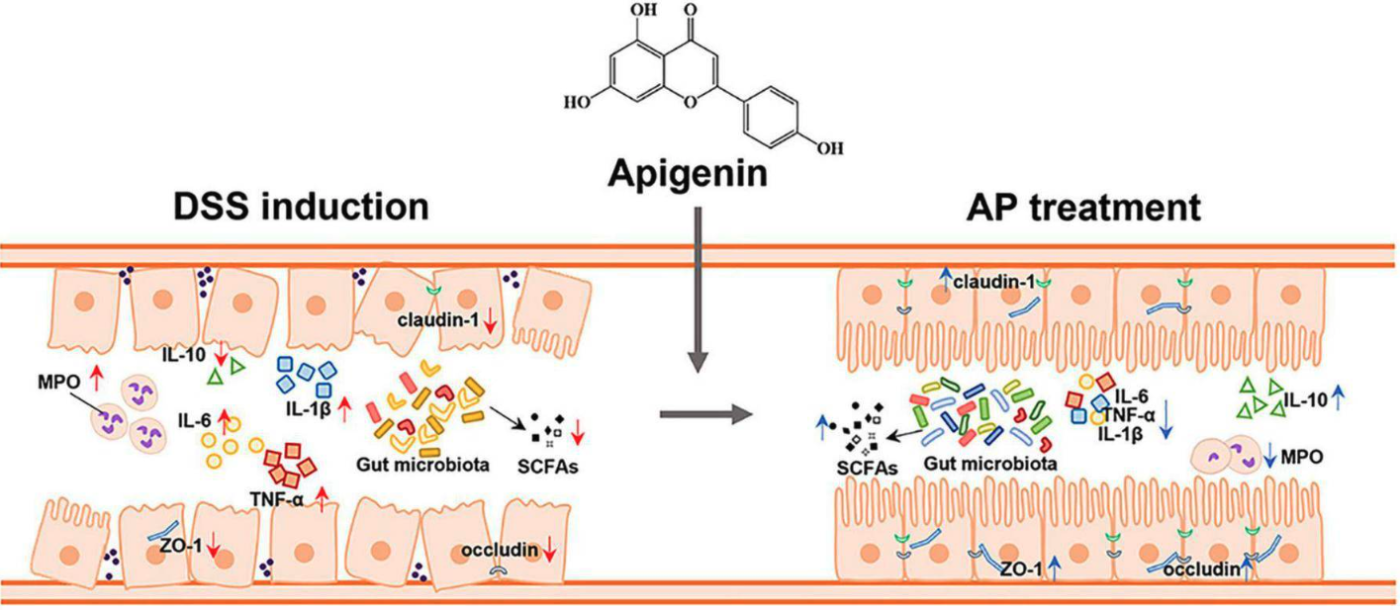
Image source: Apigenin remodels the gut microbiota to ameliorate ulcerative colitis
Apigenin reduced inflammation by decreasing the production of pro-inflammatory molecules (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and MPO) and increased the anti-inflammatory molecule, IL-10. It also increased the levels of tight junction proteins (ZO-1, claudin-1, and occludin), restored the balance of gut microbiota, and increased production of SCFAs.
Conclusion
“In conclusion, our studies indicated that apigenin, a natural functional food component, could effectively ameliorate DSS-induced UC by improving the intestine’s immune barrier function, mechanical barrier integrity, and biological barrier function in UC mice.”
