This study evaluated the safety and effects of Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) supplementation in adults with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
Key Points
- NR was safe and raised blood levels of NAD+
- Cognitive scores declined in both placebo and NR groups
- NR worsened walking speed compared to the placebo group
- NR reduced cerebral blood flow
- Subtle changes in DNA methylation were observed between placebo and NR groups
Clinical Trial Evaluates Safety and Effects of NR in Adults with MCI
Twenty adults (aged ≥ 65 years old) with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) were randomized to receive either placebo (n=10) or nicotinamide riboside (NR, n=10) for 10 weeks.
The NR group received two 250 mg doses of NR (NIAGEN, ChromaDex Inc.) orally, twice a day, for a total of 1 g daily (as tolerated).
- Dose escalation strategy: 250 mg × 1 week, 500 mg × 1 week, 750 mg × 1 week, and 1 g to end of study (6 weeks)
Study Outcomes:
- Primary: Change from baseline measures of cognition (Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA)
- Secondary: Changes in cerebral blood flow (CBF); blood NAD+ levels; and additional neurocognitive, psychometric, and physical performance tests
- Exploratory: DNA methylation in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs)
NR was Safe and Increased NAD+ Blood Levels
Supplementation with NR was well tolerated. No differences in adverse events (AEs), blood chemistry, lipid, or other measures of safety between the NR and placebo groups.
The NR group showed a 139% increase in blood NAD+ levels, represented in the figure below.
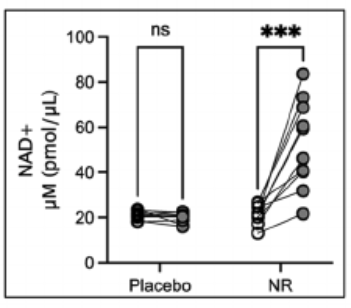
The placebo group (on the left) did not experience changes in NAD+ levels after supplementation (gray dots), compared to baseline (white dots).
In contrast, the NR group (on the right) showed significant increases in NAD+ levels after treatment (gray dots) compared to baseline (white dots).
NR Did Not Benefit Cognition
The primary measure of cognition (MoCA) declined in both placebo and NR groups over the 10 weeks:
- Placebo group: ↓ 0.89 points
- NR group: ↓ 0.3 points
The decline was slightly suppressed in the NR group, but was not statistically significant.
NR Failed to Improve Physical Function, Worsened Walking Speed
The NR group exhibited either no significant change or a slight decline in physical function measures following supplementation compared to baseline levels.
Notably, their walking speed deteriorated significantly compared to the placebo group.
In contrast, several measures of physical function were improved in the placebo group.
However, the researchers attributed these findings to the “practice effect,” where the improvement is likely due to familiarity with the test, rather than an actual change in cognitive abilities.
NR Reduced Blood Flow in the Brain
NR supplementation did not affect brain volume over the 10 week study.
“We did not observe significant changes in brain volume indicating that NR did not improve or worsen disease trajectory over the course of our 10-week study period.”
Cerebral blood flow (CBF) was significantly decreased in the NR group, depicted in the figure below.
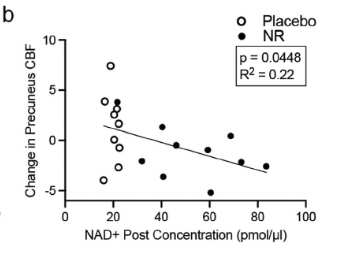
On the graph, notice that as NAD+ levels increase towards the right, there is a corresponding decrease in CBF (blood flow) shown lower on the graph. Those in the NR group (black dots) exhibit higher NAD+ levels and lower CBF compared to the placebo group (white dots)
In MCI, the brain may increase blood flow to protect itself from disease-related damage. (1)
Some studies suggest that reduced blood flow in highly active brain regions could help protect against oxidative stress, a type of damage that can occur when cells work too hard.. (2, 3)
“Therefore, the NR-associated decrease in blood flow may prevent these regions from experiencing degradation from high metabolic cost.”
However, other studies have reported decreased blood flow in MCI. (4)
“Suggesting that a further reduction with NR may be detrimental.”
As such, more research is needed to understand the impact of these findings.
The researchers note that a larger study (n=40) would yield results that would identify differences in the brain regions and help clarify the results.
Subtle Changes in Methylation Observed
While large changes in DNA methylation were not observed for either group, the researchers found the NR group seemed to gain methylation, while the placebo group lost methylation.
“While this trial was not powered to detect significant changes in DNA methylation, our analyses suggest that this NAD+ intervention may subtly alter methylation”
The researchers used several different methods to investigate the effects of NR on epigenetic aging, a process that reflects the biological age of an individual rather than just the number of years they have lived.
NR slowed down the epigenetic aging process when measured by clocks linked to lifespan and healthspan, and showed no effect when using clocks based on chronological age
Conclusion
Supplementation with NR (1 g/day) for 10 weeks did not show benefits on cognitive function in adults with MCI.
The NR group exhibited either no significant change or a slight decline in physical function measures following supplementation compared to baseline levels.
Further research with a larger sample is necessary to fully elucidate the effects on blood flow and methylation.
