This study evaluated the effects of intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of NMN on tumor-induced cellular aging, inflammation, mitochondrial function, and survival in mice.
“It’s common knowledge that NAD+ levels decrease with age. In our experiment, we treated them with NMN, resulting in stable weight gain, slower tumor progression, and longer survival periods compared to the untreated group.”
Key Points
Several benefits of NMN treatment were demonstrated:
- Reduced cellular aging through improved mitochondrial function
- Limited neuroinflammation
- Enhanced anti-tumor immunity
- Prolonged survival in tumor-bearing mice
Effect of NMN on Cellular Senesence and Survival Studied in Vitro and in Vivo
In vitro studies included healthy mouse immune cells (CD8+ T cells) and Melanoma (B16F10) cells cultured using standard protocols.
For the in vivo studies, mice were divided into 3 groups:
- Tumor-free: Healthy mice, not treated with NMN
- B16F10-bearing: Mice inoculated with mouse melanoma cells to induce tumors, not treated with NMN
- B16+NMN: Mice inoculated with mouse melanoma cells to induce tumors, NMN (i.p., 500 mg/kg every 3 days)
“We performed an intraperitoneal injection of NMN (500 mg/kg per mouse) once every 3 days in tumor-induced immunosenescence mice for 21 days.”
NMN Reduced Cellular Aging by Improving Mitochondrial Function in Immune Cells
The researchers studied how NMN impacts cellular senescence, a process where cells undergo aging and stop dividing, which is often triggered by tumors.
“The NAD+-centered mammalian aging theory suggests that NAD+ levels determine the rate and extent of aging.”
They found that the NAD+ levels in immune cells of mice with tumors decreased, but were restored when treated with NMN. This improvement was associated with:
- Reduced cell aging (senescence)
- Less inflammation
- Enhanced mitochondrial function
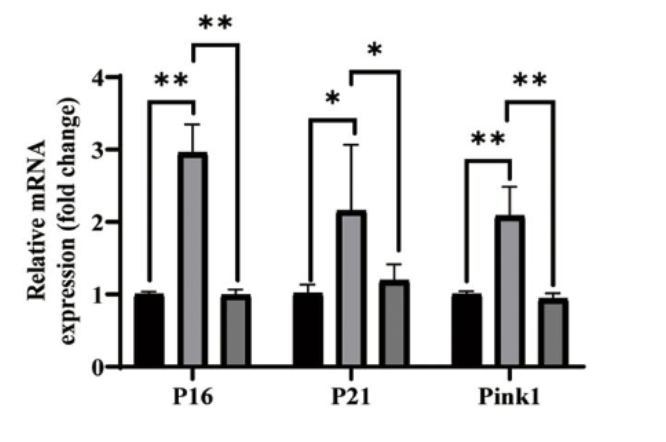
This figure shows that markers of cellular aging (P16, P21, and Pink1) are increased in immune cells from mice with tumors (light gray bar) compared to healthy mice (black bar). Treatment with NMN (dark gray bar) prevented the increase in aging markers.
“Boosting intracellular NAD+ levels with nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) prevents senescence.”
NMN Reduced Neuroinflammation in Mice with Tumors
“We then confirmed the molecular changes in vivo from different organs after NMN treatment.”
Treating mice with NMN injections (100 µM, every 3 days) led to a decrease in neuroinflammation.
“Studies have found that exogenous supplementation of NMN can repair brain damage, improve brain mitochondrial respiratory function defects, and have a certain therapeutic effect on senile degenerative diseases.”
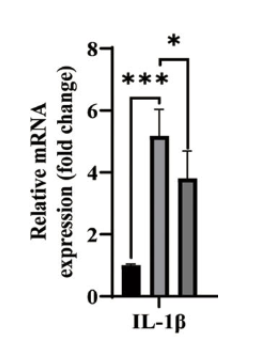
Tumor-bearing mice (light gray bar) exhibited notably higher levels of the inflammatory marker IL-1β compared to healthy mice (black bar). However, tumor-bearing mice treated with NMN showed a reduced rise in IL-1β.
Inflammation was also reduced in the liver and spleen of the mice treated with NMN.
“We observed that administration of NMN inhibited mRNA expression of IL-1β, IL-6, IFN-γ, and P21 in the brain, liver, and spleen.”
Anti-Tumor Immunity was Enhanced by NMN
NMN treatment significantly reduced tumor growth.
“Our studies suggest that preventing the generation of senescence in tumor-specific T cells is critical for antitumor immunity.”
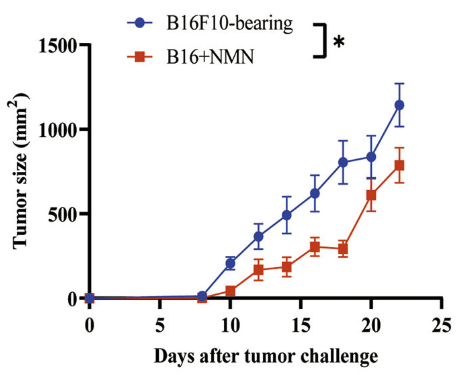
This figure illustrates that mice treated with NMN (red line) had significantly smaller tumor sizes compared to untreated mice (blue line).
“Tumor growth was significantly slowed in NMN treated mice.”
NMN Prolonged Survival in Mice
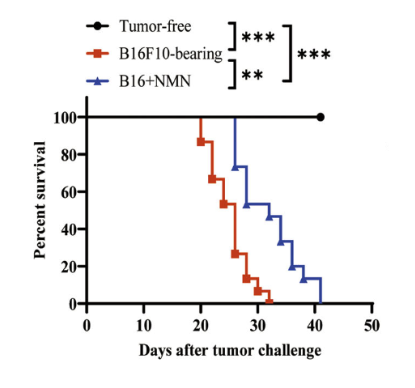
This figure shows that tumors reduced the lifespan of mice compared to healthy mice (black line). Yet, mice with tumors treated with NMN (blue line) lived significantly longer than those without treatment (red line).
“Survival analysis showed that mice treated with NMN survived longer than the other group.”
Conclusion
This research demonstrates that boosting NAD+ levels with i.p. administration of NMN may enhance mitochondrial function, inhibit inflammatory signaling pathways, decrease the rate of tumor growth, and increase the survival of tumor-bearing mice.
“Supplementing with NMN to increase NAD+ levels could enhance survival rates in mice while also reducing senescence and inflammation.”
“NAD+ supplementation is critical and beneficial in settings where NAD+ levels are low, such as tumor-bearing or normal aging.”
