This study evaluated the effects on NMN supplementation on heart function, lifespan, and NAD+ levels in a mouse model of heart failure.
Key Points:
NMN showed several benefits for mice experiencing chronic heart failure:
- Reduced markers of heart failure and prevented heart tissue scarring
- Extended lifespan
- Restored NAD+ levels comparable to those in healthy mice
Study in Mice Evaluates Effects of NMN on Heart Failure
The researchers developed a mouse model for chronic heart failure by deleting the p32 gene specifically in the heart cells (p32cKO mice). This genetic modification was chosen because it has been demonstrated to replicate chronic heart failure in previous research.
Male mice were divided randomly into four groups:
- WT: Wildtype (no genetic modification) mice with regular water
- WT + NMN: Wildtype mice with NMN (1 mg/ml) in their water
- p32cKO: Mice with heart-specific gene deletion and regular water
- p32cKO + NMN: Mice with heart-specific gene deletion and NMN (1 mg/ml) in their water
NMN supplementation started at 2 months of age and continued until 9 months of age.
Heart Function was Improved
The researchers found that NMN administration had several benefits for heart function in the mice:
- Reduced markers of proteins that are markers of heart failure
- Prevented scarring of the heart tissue
- Lowered levels of proteins associated with stress in the heart muscle
Lifespan Was Extended
This graph below illustrates the survival rate of mice in each group over the course of the experiment.
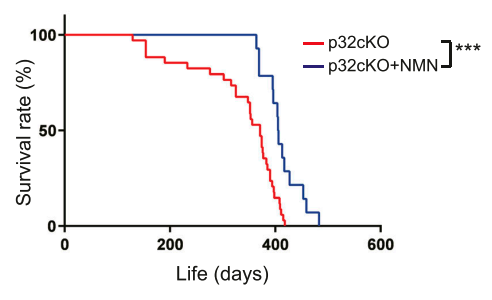
The red line represents mice with heart failure that did not receive NMN, and the blue line represents mice with heart failure that received NMN. As you move to the right of the graph, the red line drops before the blue line, meaning that the mice with heart failure that did not receive NMN died at a faster rate than the mice with heart failure that received NMN.
“We found that treatment of these mice with NMN significantly prolonged their lifespan.”
NAD+ Levels in the Heart were Restored
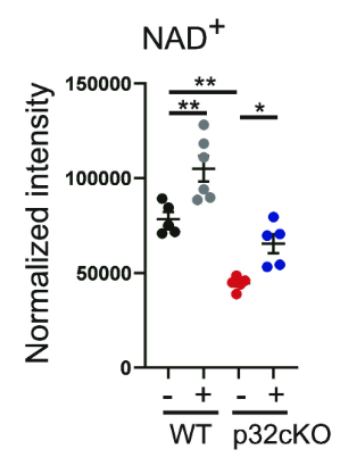
The figure on the left shows the NAD+ levels in the heart tissue of each group of mice:
- Black dots: Wildtype mice without NMN supplementation (normal mice)
- Gray dots: Wildtype mice with NMN supplementation
- Red dots: Mice with heart failure without NMN supplementation
- Blue dots: Mice with heart failure with NMN supplementation
Several findings are illustrated in the figure:
- Wildtype mice receiving NMN (gray dots) had significantly higher NAD+ levels than wildtype mice on a standard diet without NMN (black dots)
- Mice with heart failure without NMN (red dots) had significantly lower NAD+ levels than wildtype mice on a standard diet without NMN (black dots)
- Mice with heart failure receiving NMN (blue dots) had significantly higher NAD+ levels than mice with heart failure not receiving NMN; in fact, their levels were restored to levels similar to healthy wildtype mice (black dots)
“This finding indicated that myocardial NAD + levels were restored by NMN administration.”
Conclusion
This study showed that NMN supplementation protected the heart and extended lifespanc in mice experiencing heart failure.
“These results suggest that NMN treatment functionally ameliorated or prevented exacerbation of heart failure in p32 cardiomyocyte–specific knockout mice, thereby prolonging their lifespan.”
It further showed that mice NMN administration was effective in raising NAD+ levels in heart tissue.
“NAD + was decreased in p32cKO myocardium and recovered to level similar to those in the WT by NMN administration.”
