This study revealed a new technique to quickly, accurately, and inexpensively test blood NAD+ levels in humans to allow repeated testing throughout the day in clinical settings, and eventually at home.
This will make it easier for health enthusiasts to know if their NAD+ levels are lower than average, and hence more likely to benefit from strategies such as supplementation to boost NAD+ levels.
Highlights
- A new technique has been developed to rapidly and effectively measure blood NAD+ levels in humans.
- Aerobic exercise and NMN supplementation increase NAD+ levels
- Gender- and age- variations in NAD+ levels are identified
- Gene expression differences between NMN treatment responders and non-responders hint at potential tailored strategies for non-responders
Studies Using NAD+ Analyzer Showed New Insights on NAD+ Levels
The researchers conducted several experiments using the NAD+ Analyzer. The results reaffirmed previous findings, and also introduced new characterizations into NAD+ levels.
NMN Supplementation Increased Blood Level of NAD+
NMN supplementation at 500 mg per day increased NAD+ levels from 23.8 μM to 41.7 μM.
In the group receiving 1000 mg per day, levels increased from 23.8 μM to 58.8 μM.
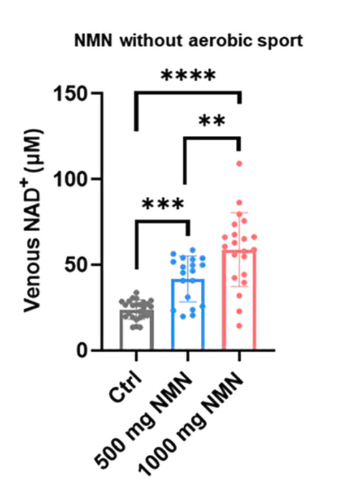
The figure to the left shows the NAD+ levels of three groups of people: those who did not receive NMN (gray bar), those who received 500 mg NMN (blue bar), and those who received 1000 mg NMN (red bar). As you can see, the NAD+ levels rise with increasing NMN dosage.
Exercise Increased NAD+ Levels and had a Greater Effect When Combined with NMN
Engaging in aerobic exercise elevated NAD+ levels from 23.8 μM to 33.8 μM.
“We showed that oral NMN supplementation and aerobic sport can significantly increase whole-blood NAD+ levels.”
The combination of NMN supplementation and exercise increased NAD+ levels from 33.8 μM to 55.5 μM.
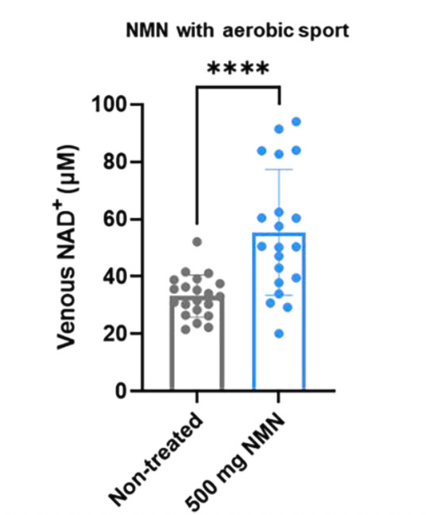
This figure shows the blood NAD+ levels of two groups of individuals who participated in aerobic sports: those who did not supplement with NMN (gray bar) and those who supplemented with 500 mg NMN (blue bar). The blue bar is significantly higher than the gray bar, indicating that supplementation with NMN increased blood NAD+ levels in aerobic athletes.
“In addition, we observed that regular aerobic sport readily increases whole-blood NAD+ levels though by a lesser extent than the NMN administration.”
Gender- and Age-Associated Differences in NAD+ Levels Were Observed
Males exhibited higher baseline NAD+ levels at 32.5 μM, compared to females at 27.2 μM.
“The cross-gender comparison indicated that females have on average a lower whole blood NAD+ level compared to males”
Differences in NAD+ Levels between gender are more pronounced in younger people.
“Moreover, the gender-related NAD+ disparity is more pronounced for participants younger than 50 years of age, but not significant for those aged over 50. “
NAD+ levels in males declined more significantly with age, decreasing from 44.2 μM to 25.9 μM, while females’ levels decreased from 32.7 μM to 24.8 μM.
“Notably, the age-related NAD+ decline is more severe for males… “
NAD+ Analyzer Studies Identify Differences Between “Responders” and “Non-Responders”
There were several people whose NAD+ levels did not respond to NMN supplementation.
“The group treated with 1000 mg/day oral NMN featured a wide distribution of the whole blood NAD+ levels (CV = 35.9%), indicating the possible non-responses towards the NMN administration.“
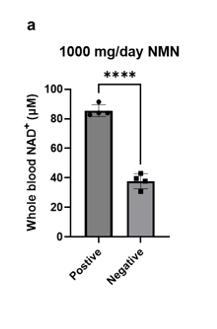
The figure to the left shows the blood levels of NAD+ in people who responded to NMN treatment (darker gray bar on the left) and people who did not respond to NMN treatment (lighter gray bar on the right).
The researchers compared the expression of genes involved in NAD+ metabolism between these two groups.
“Responders featured a higher expression of NAD+-synthesizing enzymes…,while non-responders have more expressions of NAD+-consuming enzymes…”
This may explain the wide variety of anecdotes we hear.
Possible Therapeutic Strategies For “Non-Responders”
The researchers believe non responders have more NAD+ consuming enzymes.
“RNA sequencing of PBMCs from NMN non-responders indeed indicated a higher expression of NAD+ consuming enzymes including CD38 and PARPs.”
It is suggested that identifying those not responding might be helpful to try alternative strategies, such as CD38 inhibitors.
“NAD+ precursors and modulators of its consumption pathways may be used in combination, and the convenient NAD+ blood monitoring can help to evaluate the effect of the combo therapies.”
Conclusion
This study revealed a new NAD+ analyzer that is rapid, non-invasive, and can be used to measure NAD+ levels in real-world settings.
“Here, we developed an automated NAD+ analyzer for the rapid measurement of NAD+ with 5 μL of capillary blood using recombinant bioluminescent sensor protein and automated optical reader.”
The researchers used the technique in several studies and reported several interesting findings:
- NMN supplementation and exercise increased NAD+ levels
- Males had higher NAD+ levels, but dropped more significantly with age than females
- NAD+-consuming enzymes were higher in people that did not respond to NMN treatment, indicating additional treatments, such as CD38 inhibitors, may be a potential strategy to raise NAD+ levels
“The minimal invasiveness of the assay allowed a frequent and decentralized mapping of real-world NAD+ dynamics. We showed that aerobic sport and NMN supplementation increased whole-blood NAD+ and that male on average has higher NAD+ than female before the age of 50.”
