Quercetin, a bioactive compound found in various fruits and vegetables, has attracted significant attention for its potential therapeutic effects against allergies.

Quercetin Suppresses the Allergic Response
Quercetin possesses unique properties that enable it to interact with cells in the immune system and exert anti-allergic effects.
“It has anti-allergic functions that are known for inhibiting histamine production and pro-inflammatory mediators.” (1)
Inhibits Histamine Production
Numerous scientific studies (2, 3, 4) have shed light on Quercetin’s ability to inhibit the release of histamine, a molecule that is produced by the body in response to various allergens (things like pollen, irritants, or dander).
Histamine promotes inflammation and causes unpleasant allergy symptoms (runny nose, itchy, watery eyes, sinus congestion, and sneezing), as well as related conditions such as allergic asthma and allergic dermatitis.
Reduces Inflammation and Maintains Immune Balance
“Recruitment of these inflammatory cells from the blood to the site of inflammation was regarded as a critical event in the development and persistence of airway inflammation.” (5)
Quercetin further helps alleviate allergies by lowering the levels of inflammatory cells and restoring the balance of immune cells that is disrupted during an allergic response. (2)
Research Highlight: Quercetin Improves Allergic Asthma
A recent study found that administering Quercetin to mice with allergic asthma reduced the frequency of sneezing.
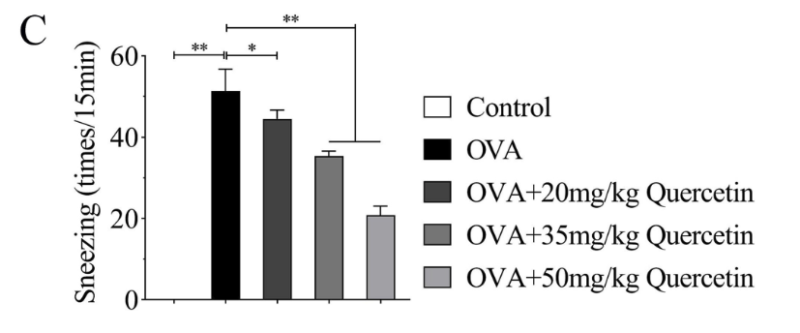
Looking at the bar graph from left to right, the bars progressively become lighter in color, representing different groups of mice receiving higher doses of Quercetin. The length of each bar represents the number of times the mice sneezed. As you increase the dose of Quercetin, the bar becomes shorter, meaning the mice sneezed fewer times.
In this study, treatment with Quercetin also reduced histamine levels, promoted immune system balance, and reduced inflammation. (2)
Reducing Inflammation Supports NAD+ Levels
The potent anti-inflammatory action of Quercetin is increasingly appreciated in the fight against inflammation, which is a common underlying factor in many health conditions. (6)
Beyond Allergy Management
“Quercetin is also a promising component that can prevent lifestyle related diseases.” (1)
In addition to benefits in the allergic response, animal studies have shown that Quercetin has anti-inflammatory effects in a variety of conditions, including high-fat diet-induced inflammation (7), obesity-associated inflammation (8), colitis (9), and arthritis (10).
Lowering Inflammation is a Strategy to Limit Consumption of NAD+
NAD+ is a molecule that is critical for cellular health. As you age, NAD+ levels decline, which makes you more susceptible to age-related diseases.
In the past decade, there has been a growing interest in finding ways to restore NAD+ levels. Researchers have identified two main approaches to increasing NAD+ levels: boosting NAD+ levels through supplementation and reducing NAD+ consumption. It is suggested that a multi-target approach that combines both of these strategies is likely to be the most effective.
Because the inflammatory process consumes NAD+, reducing inflammation is considered a critical target for persevering NAD+ levels. (11)
Anti-inflammatory compounds, such as Quercetin, help limit inflammation and reduce the consumption of NAD+.
Conclusion
Quercetin is a compound found in fruits and vegetables that has shown promising anti-allergic effects. Research shows Quercitin inhibits the release of histamine, a molecule that causes unpleasant symptoms associated with allergies. Quercetin also helps maintain balance in the immune system, which can further reduce allergy symptoms.
The anti-inflammatory effect of Quercitin has important health effects. By reducing inflammation, Quercetin helps limit the consumption of NAD+, which is a key strategy identified for restoring NAD+ levels and protecting against age-related diseases.
References
- Quercetin with the potential effect on allergic diseases
- Quercetin improves the imbalance of Th1/Th2 cells and Treg/Th17 cells to attenuate allergic rhinitis
- Quercetin inhalation inhibits the asthmatic responses by exposure to aerosolized-ovalbumin in conscious guinea-pigs
- Flavonols inhibit proinflammatory mediator release, intracellular calcium ion levels and protein kinase C theta phosphorylation in human mast cells
- Quercetin regulates Th1/Th2 balance in a murine model of asthma
- Quercetin, Inflammation and Immunity
- Quercetin transiently increases energy expenditure but persistently decreases circulating markers of inflammation in C57BL/6J mice fed a high-fat diet.
- Quercetin ameliorates metabolic syndrome and improves the inflammatory status in obese Zucker rats
- In vivo quercitrin anti-inflammatory effect involves release of quercetin, which inhibits inflammation through down-regulation of the NF-κB pathway
- Therapeutic and preventive properties of quercetin in experimental arthritis correlate with decreased macrophage inflammatory mediators
- Aging-related inflammation driven by cellular senescence enhances NAD consumption via activation of CD38+ pro-inflammatory macrophages
