This study provides a novel, highly accurate NMN measurement method and definitively confirms direct cellular transport and minute-order metabolic dynamics of NMN.
Key Points
- A new method for NMN measurement with nearly 100% efficiency was developed
- Rapid, direct transport of NMN into cells by Slc12a8 was confirmed
- Oral NMN was detected in plasma by 5 minutes, gone by 15 minutes
- NAM is the primary breakdown product of NMN in the gut, not NR or NA
- IP injection of NMN is more bioavailable than oral NMN
Advanced Methodology Accurately Measures NMN to Describe Metabolism
New methodology: Liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) with double isotopic NMN standards (double isotope-mediated LC-MS/MS (dimeLC-MS/MS)).
Cell studies: AML12 cells were treated with NMN, 78c (CD38 inhibitor), adenosine-5’-(α,β-methylene) diphosphate (AOPCP, CD73 inhibitor), 2 μM dipyridamole (ENT inhibitor), FK-866 (NAMPT inhibitor), or siRNA against Slc12a8 (knockdown of Slc12a8).
Mouse studies: Young and old mice were administered NMN via intraperitoneal (IP) injection or oral gavage, depending on their respective regimen.
New Method Accurately Measures NMN Levels
NMN blood measurements have been controversial due to conflicting test results and disagreements on the best method. Issues stem from sample handling, NMN stability during testing, and machine limitations.
“Therefore, to achieve accurate, quantitative measurements of NMN and its related metabolites, all of these issues needed to be improved.”
In this study, the researchers developed a novel method with improved instrument design to address these challenges and confirmed it was nearly 100% efficient.
“The fact that the recovery efficiency is approximately 100% for NMN strongly suggests that NMN is not degraded or altered to other related compounds such as NAM and NR in this particular procedure of sample collection and extraction.”
Uptake of NMN in Cells is Dependent on Slc12a8 Transporter
The new method was used to measure NMN uptake in mouse liver cells, which have high levels of the NMN transporter, Slc12a8.
NMN rapidly entered cells by 10 minutes, with levels steadily increasing over 2 hours.
“NMN was transported directly into AML12 cells within 10 min and also that levels of transported NMN increased up to ~30% of the endogenous NMN pool, clearly demonstrating that a significant amount of NMN can be transported directly into cells.”
To confirm the role of Slc12a8 in NMN uptake, they lowered Slc12a8 levels in the cells and examined NMN uptake, as illustrated in the figure.

NMN intake is significantly reduced in cells with reduced levels of the NMN transporter, Slc12a8, (purple line) compared to normal cells (gray line). At 60 minutes, they only take up half as much NMN, and after 120 minutes, it’s even lower at just 35%.
This suggests that Slc12a8 plays a pivotal role in transporting NMN into cells.
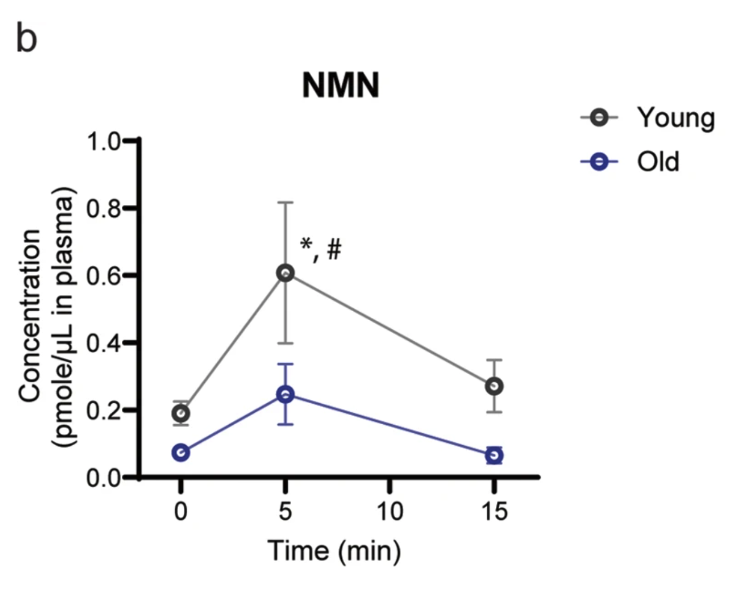
Oral NMN Detected Intact in Plasma within 5 Minutes
The researchers evaluated plasma levels of NAD+ metabolites after oral administration of NMN (300 mg/kg) in young and old mice.
“Plasma NMN levels significantly increased from 0.2 μM to 0.6 μM within 5 min and went back to basal levels by 15 min in young mice.”
This figure shows plasma NMN levels increased significantly within 5 minutes of oral administration, reaching 0.6 μM in young mice (gray line), but with lower peak levels in old mice (purple line). NMN returned to baseline by 15 minutes in both groups.
“These results definitively confirm the very fast transfer of NMN to blood circulation, as we reported previously.”
Further analysis confirmed NAM as the primary breakdown product of NMN in the gut: NAM levels increased dramatically at 5 and 15 minutes, while no changes were seen for NA and NR.
“However, at least within the time frame when NMN was rapidly transported to blood circulation, there was no significant conversion from NMN to NR. Yet, dramatic increases in plasma NAM levels were observed quickly after oral gavage, indicating that NMN is degraded to NAM in the gut.”
This clarification underscores the crucial role of minute-scale analysis, as opposed to hourly measurements, for accurately capturing the dynamics of NMN metabolism.
NMN IP Injection More Effective Than Oral Administration
Rapid elevation in plasma NMN levels were detected in young mice after IP injection of NMN (100 mg/kg), while no changes were seen in whole blood, represented in the figure below.
“Therefore, it is critical to assess plasma NMN levels, not whole blood NMN levels, and it is clear that NMN can be quickly transported to systemic circulation.”
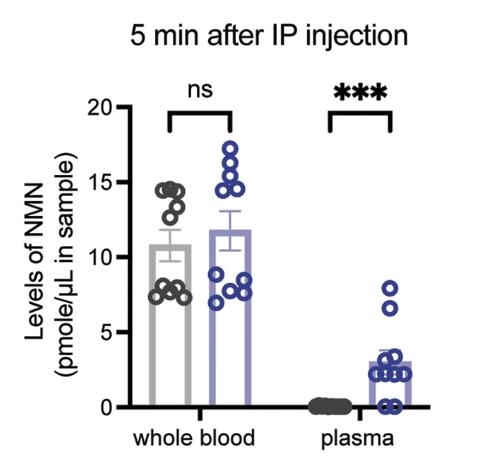
In whole blood (left side), NMN levels are similar between control (gray bar) and NMN groups (purple bar). Yet, in plasma (right side), NMN levels are notably higher in the NMN group (purple bar) compared to the control group (gray bar).
“Plasma NMN concentrations reached quite high levels 5 min after IP administration.”
Bypassing gut metabolism via IP injection significantly enhanced NMN bioavailability, leading to higher plasma levels compared to oral administration.
Conclusion
This study established an improved, accurate methodology for NMN detection, revealing rapid and direct uptake of NMN into cells.
NMN delivered orally or via IP injection resulted in swift transport to systemic circulation followed by a quick return to baseline levels.
“We have demonstrated that this methodology can accurately quantitate NMN levels in mouse plasma and confirmed quick, direct NMN uptake into blood circulation and cells.”
