A new study found injection of NAD+ using a novel liposome-like nano-particle carrier reduced overgrowth of smooth muscle cells and improved blood vessel healing in rats with narrowed arteries.
“Recently, our team successfully achieved the first in vivo NAD+-replenishing therapy, built on an innovative nano-design featuring a lipid membrane coating.”
Key Points:
- Reduced uncontrolled growth of surrounding cells
- Decreased thickening of arterial lining
- Enhanced regrowth of blood vessel lining in treated arteries
- Displayed excellent tissue response with no observed adverse effects
Injected NAD+ In Nanoparticles To Improve Artery Widening Outcomes
This study used a rat model of narrowed arteries to determine effectiveness of nanoparticle NAD+ to improve recovery.
Healthy rats undergoing a common artery-widening procedure were divided into treatment groups:
- Saline (control)
- NAD+ encased in liposome-like nanoparticles
- Free NAD+ solution
- Empty nanoparticle carrier
Treatments were delivered via a single intravenous injection immediately following the artery-opening procedure.
The NAD+ nanoparticles used closely resemble liposomes in structure and function, with comparable bioavailability. Researchers chose this delivery method partially due to high absorption rates, using 1/10 the typical dosage.
Nanoparticle NAD+ Delivery Helps Protect and Regenerate Blood Vessels
Targeted delivery of NAD+ via liposome-like nanoparticles inhibited overgrowth of surrounding muscle cells, a primary contributor to arteries becoming re-blocked over time.
Treatment simultaneously protected and regenerated cells lining blood vessels.
“The [nanoparticle coating] overcomes NAD+’s intrinsic limitations by protecting it from degradation and enabling direct intracellular NAD+ delivery through the endocytic pathway.”
The figure below shows the thickness of the tissue lining the arteries of the rats after widening and NAD+ treatment.
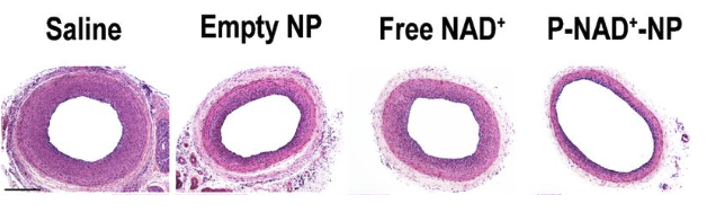
From left to right, this figure illustrates the outcomes in each of the four groups.
-
- Saline: The saline control group shows the thickest blood vessel lining indicating tissue thickening and cell overgrowth.
- Empty NP: This group received nanoparticles without NAD+. The lining appears slightly thinner than the control, suggesting a possible minor effect, but not statistically significant.
- Free NAD+: This group received free NAD+. The lining shows no noticeable difference compared to the control, indicating no effect from free NAD+.
- P-NAD+-NP: This group received nanoparticle-encased NAD+. The vessels have the thinnest lining, demonstrating the most effective reduction in tissue thickening and cell overgrowth.
“Our technology enabled outstanding preclinical efficacies at mere 1/10 or less dosage (10 mg/kg) with mere one dose over the course of 2 weeks.”
Nanoparticle NAD+ Facilitates Blood Vessel Healing and Reduces Risk of Repeated Artery Blockages
Animals treated with the nanoparticle NAD+ showed:
- Significant reduction in muscle cell overgrowth
- Accelerated healing of blood vessel lining
- No significant adverse effects, indicating high safety profile
Conclusion
NAD+ encased in liposome-like nanoparticle envelopes, not free NAD+, effectively mitigates the cell overgrowth and thickening of blood vessel lining seen after an artery-widening procedure.
This treatment promoted tissue recovery and improved circulatory outcomes.
“The combined innovation allowed us, for the first time, to probe targeted NAD+ repletion as a new avenue in achieving differential management of the two seemingly opposite objectives: anti-restenosis (inhibiting SMC proliferation) and re-endothelialization (promoting EC regeneration).”
