Previous human clinical trials have shown that NAD+ levels can be safely and efficiently replenished by oral NMN supplementation. Until a recent study, however, the safety and efficacy of intravenous NMN had not been firmly established.
Intravenous NMN shown to be safe and effective
Using 10 healthy volunteers, results indicated that intravenous NMN is both safe and effective in humans. Although IV administration can pose a higher risk of damage to major organs, NMN IV did not affect electrocardiograms, pulse, or blood pressure, nor did it affect metabolic markers in the liver, heart, pancreas, or kidneys.
“These results indicate that intravenous NMN administration is safe and beneficial in humans.” (1)
“we speculated that NMN could be safely administered intravenously, as it is a metabolite produced in the body” (1)
NMN IV dramatically reduced triglyceride levels
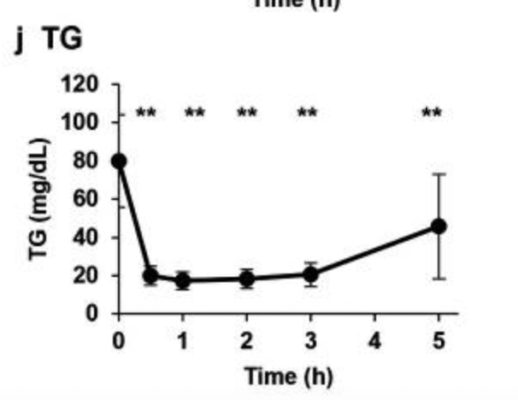 After administration of just 300mg of NMN by IV, NAD+ levels rose significantly while triglyceride levels decreased dramatically.
After administration of just 300mg of NMN by IV, NAD+ levels rose significantly while triglyceride levels decreased dramatically.
This occurred without damaging blood cells or raising low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels in the blood.
These results were dramatically different than oral NMN supplements, which suffer from poor bioavailability that intravenous NMN does not and demonstrates the potential for far more benefit if more bioavailable methods are used.
“NMN administration significantly increased blood NAD+ levels without damaging blood cells and significantly reduced blood triglyceride (TG) levels” (1)
NMN IV could be effective treatment for diseases associated with elevated TG levels
The findings suggest that NMN IV is not only an effective method of reducing TG levels but can also be effective at prevention and treatment of diseases associated with increased TG levels, such as fatty liver and diabetes.
“These findings imply that intravenous administration of NMN may lead to the prevention and treatment of diseases associated with increased TG levels, such as fatty liver and diabetes.” (1)
NNM IV stimulates more natural production of NAD+
The study found that NAMPT levels are increased by intravenous administration of NMN. NAMPT is an enzyme responsible for converting nicotinamide into NAD+ in a recycling process called the salvage pathway.
“Since NAMPT levels are increased by intravenous administration of NMN, it is expected that NAD may be continuously synthesized via the salvage pathway with a single administration. “
This discovery means that NMN IV can lead to greater production of NAD+ by enhancing the body’s own, natural conversion processes. Coupled with the dramatic reduction to triglyceride levels, NMN IV may help to improve obesity and slow the aging process.
References:
