This study evaluated the safety and effects of high-dose (3,000 mg) Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) supplementation in patients with Parkinson’s Disease (PD).
Key Points:
- High-dose NR was safe for 28-day supplementation
- NR significantly impacted NAD+ metabolome
- Changes in medication timing hindered assessment of NR’s clinical effects
- Mild, but significant, homocysteine elevations were observed
- NR did not affect methyl-group pools or cardiovascular parameters
Clinical Trial Evaluates Safety and Effects of High Dose NR in Patients
The was a 4-week phase I, single-center, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial.
Twenty patients with PD were randomized into two groups (n = 10 per group):
- NR group: Received 1500 mg NR twice daily
- Placebo group: Received placebo capsules
While not statistically significant, the researchers acknowledged that the NR group was slightly younger, and had a slightly lower BMI, fewer years since diagnosis, and higher baseline MDS-UPDRS on average.
Study Outcomes:
- Primary: Incidence of treatment-associated moderate and severe adverse events (AEs)
- Secondary: Difference in treatment-associated mild AEs, change in the clinical severity of PD, measured by the Movement Disorder Society Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS), and changes of the NAD metabolome in blood and urine between groups
- Exploratory: Difference in the change of serum homocysteine levels and of fasting blood glucose and serum insulin levels between groups
Patients were evaluated by a movement disorder specialist at baseline (visit 1, V1), day 7 (V4), day 14 (V5), day 21 (V6) and day 28 (V7).
High-Dose NR Treatment was Well Tolerated
NR supplementation (3,000 mg/day) for 4 weeks was safe and well-tolerated in Parkinson’s Disease (PD) patients, with no moderate or severe AEs, NR-attributed mild AEs, or signs of toxicity observed.
“NR doses up to 3000 mg daily do not need to be gradually increased and can be initiated directly in NR-naïve individuals.”
Medication Timing Hindered Symptom Evaluation
While the researchers noted positive effects of NR on clinical symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease (PD), the NR group had a shorter time interval from their last dose of dopaminergic medication at the final visit in comparison to baseline.
“NR-treatment improved clinical symptoms of PD, measured by MDS-UPDRS, while this remained unchanged in the placebo group.”
However, the impact of the medication (levodopa) on motor symptoms in PD is substantial, offering the NR group a slight advantage in the assessment.
“The possibility that the observed effect is attributed to levodopa cannot be confidently excluded.”
NR Treatment Significantly Modulated the NAD Metabolome
High-dose NR supplementation had a significant impact on the NAD metabolome.
“At a dose of 3000 mg daily, NR treatment greatly augmented the NAD-metabolome, including a ~3.7-fold (range 1.8–5.8-fold) increase in whole blood NAD+ levels.”
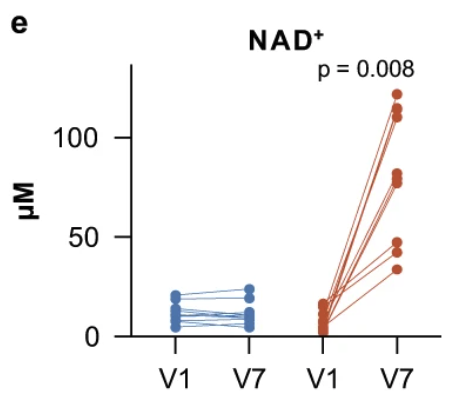
This figure shows the blood levels of NAD+ in the placebo group (blue) did not change from baseline (visit 1, V1) to day 28 (visit 7, V7). In contrast, the NR-group (red) showed significant increases in blood NAD+ levels between baseline (V1) and day 28 (V7).
Serum Homocysteine Levels Increased With NR Treatment
High levels of the amino acid, homocysteine, have been linked to health issues. (1, 2, 3)
This figure shows that serum homocysteine levels were higher in the NR group (red box) compared to the placebo group (blue box).
“NR treatment was associated with a mild but significant increase in serum HCy levels.”

High Dose NR Did Not Deplete Methyl-Group Pool
Methylation, the transfer of a methyl group to a molecule, is a crucial cellular process essential for human health and longevity.
The breakdown of NAD+ precursors requires methyl group donations, which has raised concerns about potential methyl pool depletion with high-dose supplementation.
Several markers of methyl-group pool status confirmed that NR supplementation at 3,000 mg/day did not affect methyl group levels.
The figure below shows the blood levels of the major methyl-group donor, S-adenosylmethionine (SAM).
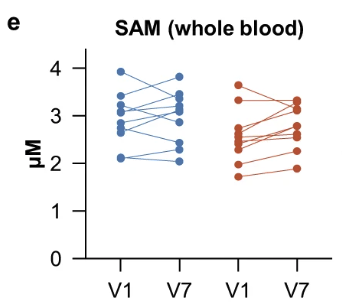
No changes in SAM were observed from baseline (V1) to day 28 (V7) in the placebo (blue) or NR (red) groups.
“NR even at a dose of 3000 mg for 4 weeks does not cause depletion of the methyl-group pool.”
NR Did Not Change Blood Fats or Blood Pressure
Previous NR clinical trials (1, 2) have shown mild increases in blood fats, which was not observed in this study.
While a previous NR clinical trial demonstrated improvements in blood pressure, this effect was not replicated in the current study. The researchers note that blood pressure regulation can be impaired in Parkinson’s Disease (PD).
Conclusion
A high-dose of nicotinamide riboside (NR) for four weeks is well tolerated and significantly modulates the NAD+ metabolome in patients with Parkinson’s Disease.
However, mild, but significant elevations in serum homocysteine were observed.
The high dose of NR did not deplete the methyl-group pools.
“These findings support the possibility of extending the dose range of NR up to 3000 mg in clinical trials, provided adequate safety monitoring.”
