In a new study by Brown University School of Medicine, it was shown that oral nicotinamide (NAM) supplementation decreased the incidence of keratinocyte carcinoma (KC) in high-risk skin cancer patients. NAM is converted to NAD+ in the body and it is NAD+ that is believed to be responsible for for the decrease in Keratinocyte carcinoma risk.
NMN and NR lead to greater increases in NAD+ than NAM
It has been well established that the molecules NMN and NR lead to greater increases in NAD+ levels than NAM, so scientists in this study hypothesized that oral supplementation with NMN or NR can lead to even greater reductions in Keratinocyte carcinoma than NAM.
“Research into cellular metabolism and aging suggests that NR and NMN can lead to greater increases in NAD+ vs NAM” (1)
“We hypothesize that oral supplementation with NR or NMN may lead to greater reductions in KC than NAM” (1)
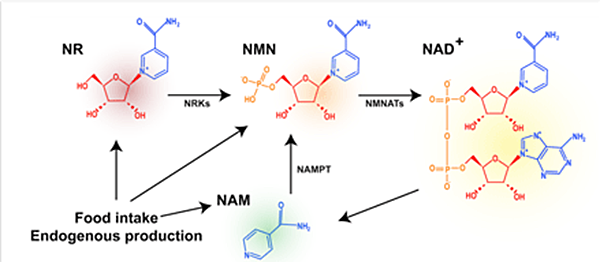
.
NMN and NR repair DNA and decrease cancerous mutations
NAD+ has many protective cellular qualities, including fueling DNA repair, which help prevent cancerous mutations. As we age, we produce less and less NAD+, which is a big contributor to the many diseases of old age.
“Nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) are NAD+ intermediates like NAM; however, their protective roles on cellular DNA and effects on cancer have been under-explored” (1)
“reduced NAD+ may be one causative factor in age-associated functional decline and disease” (1)
“NR and NMN are safe and well-tolerated and are consequently currently undergoing investigation as agents able to protect against age-associated disease caused by NAD+ depletion” (1)
NAD+ decreased frequency of actinic keratoses and keratinocyte carcinomas in high-risk patients
In the study, NAD+ was found to decrease the size, number, and frequency of actinic keratoses (AK’s). AK’s are rough, scaly patches on the skin that develop in high-risk cancer patients after years of exposure to the sun.
After treatment with NAM to boost NAD+ levels in 386 high-risk cancer patients, NAD+ also demonstrated a significant 23% reduction in the frequency of new Keratinocyte carcinomas vs placebo.
NAD+ further depleted by ultraviolet radiation (UV) exposure
In addition to age-related depletion of NAD+ stores, ultraviolet radiation (UV) exposure can cause a further drop in NAD+ levels. This leads to inhibition of glycolysis and a reduction of energy-producing ATP.
This reduction in ATP means that there is less energy for DNA repair, predisposing cells to oncogenic DNA damage and tumor formation.
NAD+ increased DNA repair and reduced UV-induced inflammation
Keratinocytes supplemented with oral NAM not only showed increased NAD+ levels but also showed increased DNA repair and reduced UV-induced inflammation. This led researchers to the hypothesis that NAD+ supplementation may:
“replenish depleted NAD+ found in states associated with UV exposure, ultimately replenishing cellular ATP and promoting the repair of damaged DNA” (1)
“Animal models indicate that NAD+ deficiency increases cellular sensitivity to UV light, exhibits impaired ability to repair damaged DNA, and has increased genomic instability” (1)
This theory has garnered widespread acceptance and is now considered the primary proposed mechanism for NAD’s effect for reducing Keratinocyte carcinoma.
References:
