This study compared the effects of standard and liposomal Resveratrol on kidney damage, oxidative stress, and inflammation in diabetic rats.
“Liposomal encapsulation protects resveratrol from degradation in the digestive system, ensuring more of the active compound reaches the bloodstream and, ultimately, the kidneys.”
Key Points
The study highlighted key findings on standard (R) and liposomal Resveratrol (LR):
- LR outperformed R in improving blood markers of kidney health
- LR most effectively reduced inflammatory molecules
- Both R and LR reduced fat oxidation
- LR increased activity of antioxidant enzymes, R did not
- Both LR and R promoted cell survival
- LR was most effective in restoring kidney function
Effects of Liposomal and Standard Resveratrol Compared in Diabetic Rats
A diabetic rat model was used to evaluate the therapeutic potential of LR and R on kidney damage, inflammation, and oxidative stress.
Rats were injected with streptozotocin (STZ), a chemical that destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, to induce diabetes.
The rats were divided into five groups for the 5-week study:
- Control: Healthy rats (No STZ or treatment given)
- Diabetes (STZ): Diabetic control rats (STZ, i.p.; no treatment)
- STZ + LR (20 mg/kg): Diabetic rats (STZ, i.p.; LR, 20 mg/kg/day, oral)
- STZ + LR (40 mg/kg): Diabetic rats (STZ, i.p.; LR, 40 mg/kg/day, oral)
- STZ + R (40 mg/kg): Diabetic rats (STZ, i.p.; R, 40 mg/kg/day, oral)
LR Showed Superior Impact on Kidney Health Markers
Over time, high blood sugar damages kidney cells and blood vessels.
In this study, diabetic rats exhibited decreased protein levels and elevated kidney toxicity markers.
Protein levels were improved across all Resveratrol treatment groups.
Notably, LR (40 mg/kg) was the most effective for reducing markers of kidney toxicity.
“LR at 40 mg/kg was more effective than LR at 20 mg/kg and resveratrol alone in reducing creatinine and urea levels and improving kidney histopathology in diabetic rats.”
The figure below shows the level of urea in the blood, a waste product from protein metabolism that the kidneys remove; elevated levels may signal kidney dysfunction.
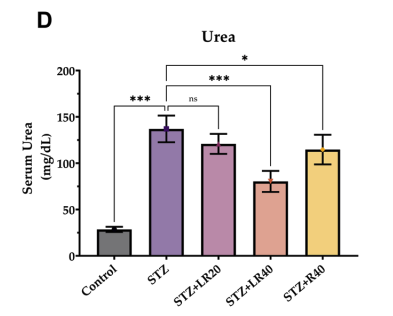
The untreated diabetic rats (STZ, purple) had significantly higher urea levels than healthy rats (Control, gray). Treatment with 40 mg/kg LR (STZ+LR40, orange) was the most effective in reducing urea levels in diabetic rats.
“These results suggest that LR, particularly at a higher dosage, may have a beneficial effect in ameliorating nephrotoxicity associated with diabetes.”
“Our results are consistent with previous reports showing that LR and resveratrol treatment reduces creatinine, urea, and BUN levels in diabetic rats.”
LR was More Effective for Combating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
High-dose LR significantly reduced levels of inflammatory compounds (TNF-α, IL-6, and NF-κB).
“Interestingly, administering LR at the higher dose resulted in a striking suppression (p<0.001) of these inflammatory mediators, bringing their levels back to baseline.”
While R and the lower dose of LR also reduced inflammatory markers, the higher dose of LR was significantly more effective.
“Resveratrol alone (40 mg/kg) also reduced these markers but was less effective than LR.”
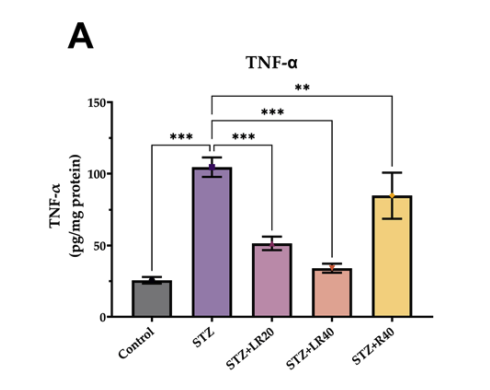
This graph shows that diabetic rats (STZ, purple) had higher levels of the inflammatory molecule, TNF-α, compared to healthy rats (Control, gray). Treatment with 40 mg/kg LR (STZ+LR40, orange) was most effective in reducing TNF-α levels.
Oxidative stress, measured by MDA levels, decreased across all Resveratrol treatment groups.
However, only LR-treated groups (20 and 40 mg/kg) significantly boosted the activity of key antioxidant enzymes, catalase and GPx.
“The administration of LR at doses of 20 and 40 mg/kg led to a notable elevation in enzyme activity by 1.6-fold (p<0.001) and threefold (p<0.001), respectively, following a dose-dependent pattern.”
The standard formulation, R, did not impact enzyme activity.
“In contrast, the sole administration of resveratrol did not yield a significant restoration (p>0.05) of enzyme activity in diabetic rats compared to the control group.”
Resveratrol Promoted Cell Survival
Diabetic rats exhibited changes in protein levels associated with cell health, reflecting kidney dysfunction:
- Increased levels of proteins linked to cell death (caspase-3 and BAX)
- Decreased levels of a protein that promotes cell survival (BCL-2)
All Resveratrol treatment groups showed a significant reduction in caspase-3 and BAX levels, along with a restoration of BCL-2 levels to near-normal.
“The anti-apoptotic effects of LR are likely due to its ability to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which are two key drivers of apoptosis.”
Higher-dose LR Reversed Kidney Damage Most Effectively
Analysis of the kidneys of untreated diabetic mice showed significant damage:
- Thickened Kidney Structures: The tiny filtering units (glomeruli) became scarred and thickened
- Tissue Overgrowth: Excess growth of support cells and material in the kidneys
- Cell and Tissue Damage: Signs of cell death, tissue breakdown, and shrunken kidney filters
- Inflammation: Immune cells infiltrating the kidneys, indicating inflammation
Rats treated with the lower dose of LR (20 mg/kg) showed moderate improvements in kidney damage, while those treated with the higher dose (40 mg/kg) experienced near-complete restoration of kidney health.
“Compared to 20 mg/kg and resveratrol alone, treatment of LR at 40 mg/kg showed better results in improving kidney damage by attenuating histopathological alterations.”
“These findings underscore the significant improvement in diabetic kidney damage achieved with LR at a dosage of 40 mg/kg/day.”
Conclusion
The study demonstrated Resveratrol’s potential in diabetes-related kidney damage, with the liposomal formulation (LR) proving more effective than standard Resveratrol (R).
“Our findings emphasized the enhanced effectiveness of LR in ameliorating hyperglycemia-induced kidney damage compared to resveratrol alone, although the latter still demonstrated a more significant effect than the vehicle-treated diabetic animals.”
Specifically, LR was more effective in reducing oxidative stress. Inflammation, and markers of kidney toxicity in the rats.
“Compared to resveratrol alone, LR has shown a more pronounced inhibition of NF-κB activation and nuclear translocation, leading to more effective suppression of pro-infammatory cytokines and genes associated with oxidative stress.”
“Higher doses of LR (40 mg/kg) were more effective in reducing nephrotoxicity markers than lower doses or resveratrol alone”
The higher-dose LR treatment nearly completely restored kidney damage, outperforming other treatments.
“Notably, a reversal of the histological abnormalities induced by streptozotocin was evident in the renal cortex sections of diabetic rats treated with the higher dose of LR.”
The enhanced efficacy of the liposomal formulation suggests improved absorption and bioavailability.
“Our results also demonstrate significant improvement in kidney function in diabetic rats treated with LR at both 20 mg/kg and 40 mg/kg, suggesting that the liposomal formulation enhances resveratrol’s absorption and bioavailability.”
