This study evaluated the efficacy of liposomal Berberine on insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, and liver function in diabetic rats.
“The pharmacological properties of berberine … include protection against neurodegeneration, cardiovascular disease, liver disease, high cholesterol, diabetes, and atherosclerosis.”
Key Points:
Liposomal Berberine was found to have a number of beneficial effects in diabetic rats:
- Glucose metabolism was stabilized
- Lipid levels were normalized in the blood
- Balance of inflammatory molecules was improved
- Protection from diabetes-associated damage in the liver
Study Evaluates the Effects of Liposomal Berberine on Metabolic Complications Associated with Diabetes in Rats
The researchers randomly assigned 50 rats to five groups of 10 rats each.
The control group was given a standard saline solution (0.5 mL/rat). The researchers used the high-fat-diet STZ model to induce Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in the remaining four groups.
The diabetic groups were then given either standard saline (0.5 mL/rat), liposomal Berberine (Lip-BBR, 10 mg/kg b.wt), vildagliptin (Vild, a well-established anti-diabetic drug, 10 mg/kg b.wt), or a combination of Lip-BBR (10 mg/kg b.wt) and Vild (5 mg/kg b.wt).
“Nano liposomes incorporated in BBR (Berberine) are efficient for improving bioactive solubility, thus enhancing bioavailability and stability.”
The treatments were administered orally once daily for 14 weeks.
Liposomal Delivery of Berberine
Berberine is poorly absorbed and has low bioavailability, which poses a challenge for researchers to fully elucidate its potential therapeutic effects.
“Studies showed that less than 1% of orally administered BBR is totally accessible in rats.”
To overcome this issue, the researchers employed a liposomal delivery system, enclosing and safeguarding Berberine in liposomes for safe and effective delivery throughout the body.
“Liposomal encapsulation of berberine (Lip-BBR) plays a vital role in its oral administration, significantly enhancing its therapeutic effectiveness.”

Pictured above: Liposome-Encapsulated Berberine. The researchers characterized the Liposome-Encapsulated Berberine preparation using a scanning electron microscope.
Liposomal Berberine Stabilized Glucose Levels
The results showed that Liposomal Berberine (Lip-BBR) and vildagliptin (Vild) significantly reduced blood glucose levels in diabetic rats compared to untreated diabetic rats.
The combination of Lip-BBR and Vild had a stronger effect than either treatment alone.
“Interestingly, the combination of both treatments (Lip-BBR and Vild) in diabetic rats demonstrated significantly (p < 0.001) lowered glucose levels than the single-treated groups.”
Lip-BBR also significantly reduced serum insulin levels and HOMA-IR.
Cholesterol and Triglyceride Levels Were Improved
Rats with T2DM developed dyslipidemia. They had lower levels of HDL, and higher levels of LDL, total cholesterol (TC) and triglycerides (TG).
Lip-BBR prevented the progression of dyslipidemia. Rats showed significantly higher levels of HDL and reduced levels of TC, LDL, and TG.
Liposomal Berberine Improved the Balance of Inflammatory Proteins
Levels of cytokines were measured in order to test the effects of Lip-BBR on inflammation.
- Lip-BBR increased serum levels of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 by 37%
- Lip-BBR reduced the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 by 56% and TNF-a by 50%
“Lip-BBR was shown to reduce TNF-a and IL-6 levels while increasing IL-10 and ameliorating the inflammatory state imposed on T2DM induction in rat liver tissue, as demonstrated by the current data.”
Liver Injury Was Reduced
Lip-BBR protected the rats against diabetes-associated liver damage.
Lip-BBR significantly reduced the levels of liver enzymes (ALT, AST, and ALP) that are used as indicators of liver function. When combined with Vild, the enzyme levels were nearly as low as those in non-diabetic rats.
The researchers also found Lip-BBR protected against oxidative stress.
The figure below illustrates the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) in the livers of rats in each group.
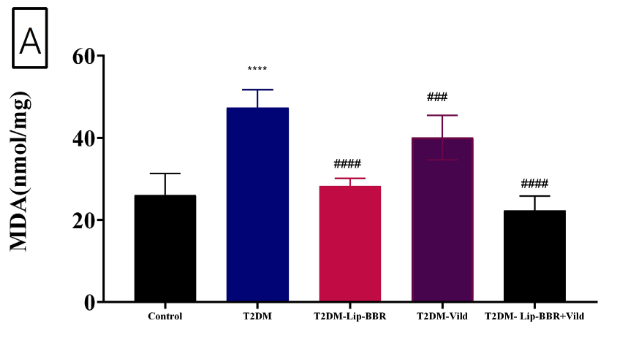
- Control group (black bar, left): Rats without diabetes, given saline solution
- T2DM group (blue bar): Rats with diabetes, given saline solution. Their MDA levels were almost two times higher (1.93 folds) than non-diabetic mice
- T2DM-Lip-BBR group (pink bar): Rats with diabetes, given Lip-Ber. Their MDA levels are much lower than the untreated T2DM group
- T2DM-Vild group (purple bar): Rats with diabetes, given vildagliptin (Vild), an anti-diabetic drug. Their levels of MDA are lower than the untreated T2DM group.
- T2DM-Lip-BBR+Vild group (black bar, right): Rats with diabetes, given both Lip-BBR and Vild. Their levels of MDA are near the levels observed in non-diabetic mice.
Lip-BBR also significantly increased levels of the antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, and catalase in the livers of diabetic rats.
Additionally, treatment with Lip-BBR reduced liver lesions caused by steatosis (fat buildup), cell death, and inflammation.
Conclusion
This study showed that oral administration of Berberine via liposomes significantly protected rats from metabolic complications associated with diabetes.
“In an animal model of type 2 diabetes, the intragastric delivery of Lip-BBR via liposomes exhibited remarkable protective effects against hepatic tissue damage, steatosis, inflammation, insulin resistance, and hepatocellular enzyme imbalance.”
