Tag Archives: nr
“In comparison to NAD+ IV, NR IV was infused faster, and the infusion experience was more tolerable.”
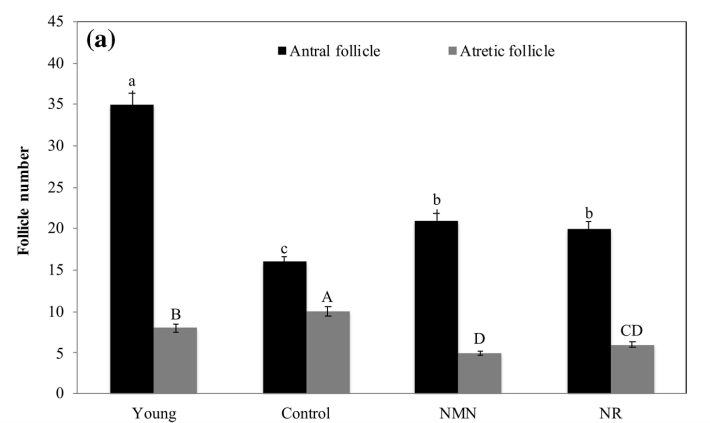
A recent study investigated the effects of NMN and NR on ovary health and function in middle-aged rats. “This study reveals that NMN alone or NR alone can rebalance mitochondrial dynamics by decreasing excessive fission in middle-aged rat ovaries, thus alleviating mitochondrial stress and correcting aging-induced folliculogenesis abnormalities.” This graph shows the number of healthy […]
"Liposome-based NR loading is an effective strategy for improving the pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of NR, especially to the brain."
While all three precursors – Niacin, NR, and NMN – elevate NAD+ levels, their journeys within the body are distinct. Understanding these individual pathways is crucial, as they may have significant effects on outcomes beyond just the NAD+ level itself.
“We have demonstrated that this methodology can accurately quantitate NMN levels in mouse plasma and confirmed quick, direct NMN uptake into blood circulation and cells.”
This study evaluated the safety and effects of high-dose (3,000 mg) Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) supplementation in patients with Parkinson’s Disease (PD).
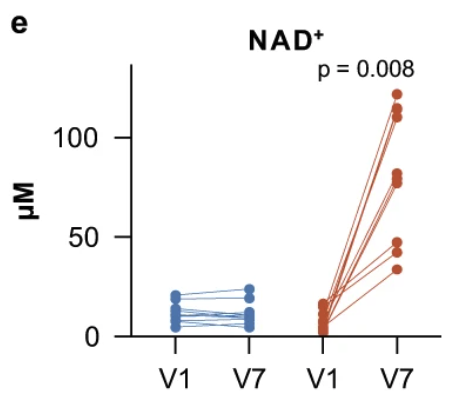
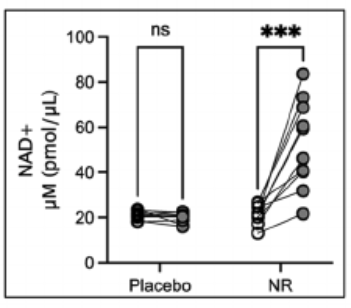
This study showed that NR (1 g/day) for 10 weeks is safe in adults with MCI and effectively increased blood levels of NAD+.
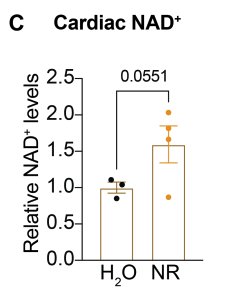
Circadian rhythm is your body’s internal clock that permits anticipation of daily patterns, regulating when it’s time to sleep, wake up, eat, and digest. This study evaluated the effects of NR supplementation on age-related changes in the heart’s circadian rhythm.
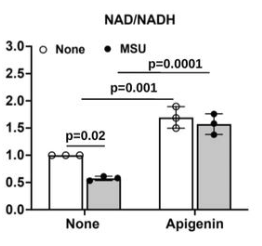
This study evaluated the effects of Apigenin and Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) on factors associated with gouty arthritis.
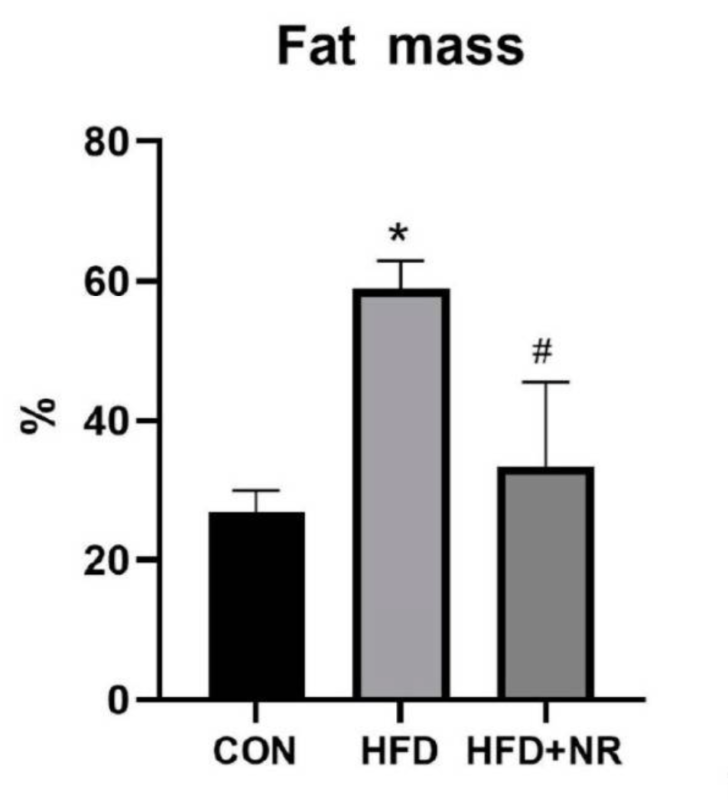
This study showed that NR supplementation protected mice from HFD-induced metabolic dysfunction, specifically through protecting mitochondrial function in the skeletal muscle.
- 1
- 2