This study evaluated the effects of intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of NMN on tumor-induced cellular aging, inflammation, mitochondrial function, and survival in mice.
Author Archives: Rebecca Crews
“NMN had the highest concentrations in breast milk among the NAD-related substances. We demonstrated, for the first time, a positive relationship between NMN concentrations in breast milk and the neurodevelopmental outcome of a child.”
“We have demonstrated that this methodology can accurately quantitate NMN levels in mouse plasma and confirmed quick, direct NMN uptake into blood circulation and cells.”
This study evaluated the effects of NAD+ injections in patients with heart failure.
“NMN exerts neuroprotective effects after SCI by the regulation of certain genes acting on signaling pathways related to neurological diseases.”
This study found that injection of NMN protected mice from asthma-induced inflammation, mucus production, and lung barrier disruption.
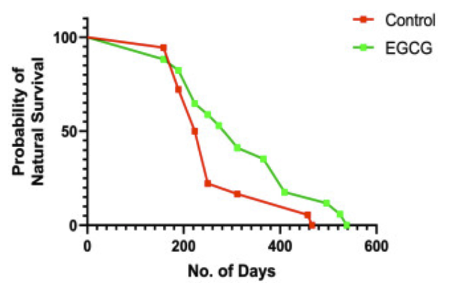
This study found that the continued administration of Green Tea Catechin (EGCG) improves the lifespan, cellular health, and cell waste clearance in aging mice.
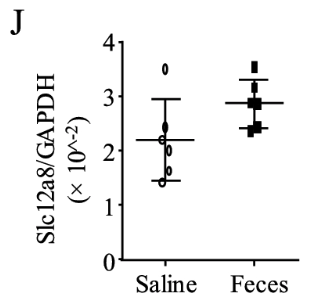
Sepsis-associated disruption of the NRK1/2 pathway for NAD+ synthesis emphasized the critical role of NMN transport through the Slc12a8 transporter.
NAD+ deficiency is not just a concern of aging; it also plays a significant role in the development of various chronic diseases that are on the rise among younger generations.
Hyaluronic acid (HLA) is a naturally occurring gel-like substance that the body produces. It is abundantly present in the skin, joints, and eyes, where its exceptional ability to attract and retain water plays a crucial role in maintaining tissue hydration and lubrication.
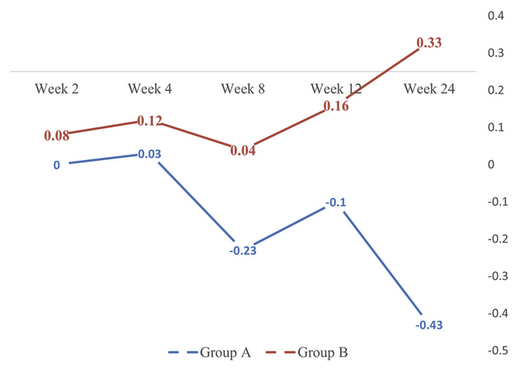
“This study shows that Liposomal Blend is a vehicle with the ability to enhance the anti-aging properties of the ingredients within the facial serum by facilitating its delivery into the underlying layers of the skin.”
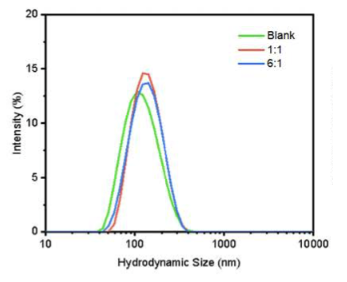
The study developed a novel microfluidic approach to co-encapsulate NMN and an anticancer drug, honokiol (HNK), in liposomes and established a new HPLC method for NMN encapsulation quantification.