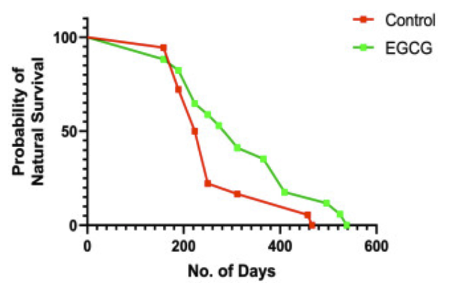
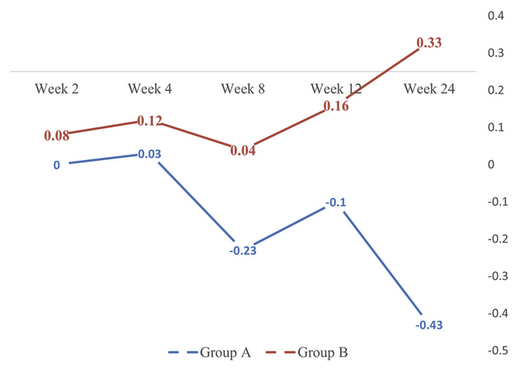
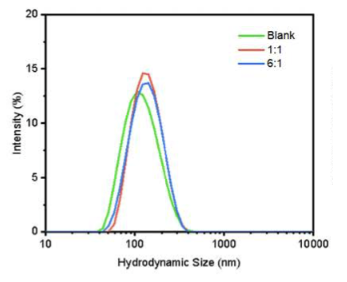
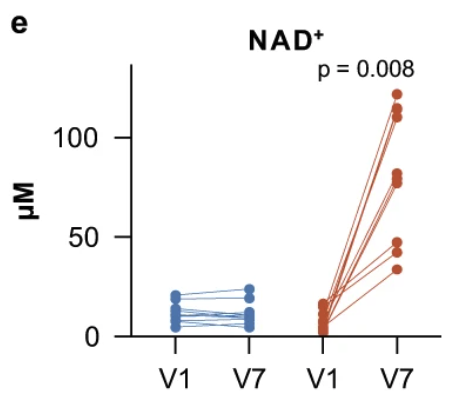
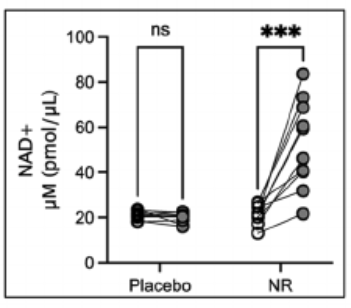
This study evaluated the effects of NAD+ injections in patients with heart failure.

Updated list of NMN studies in humans
The pace of NMN human trials has been steadily increasing over the past year, moving past initial stages proving NMN is safe to use in humans. Check out our updated list & study summaries.
See All Studies
NMN Resveratrol synergy
A study shows the combination of NMN & Resveratrol work synergistically to nearly double NAD+ levels!
READ MORE
intravenous nmn results
A study on Intravenous NMN resulted in a massive decrease in blood triglyceride levels. Could liposomal NMN have similar results?
READ MORE