This study evaluated the effects of NAD+ injections in patients with heart failure.
Category Archives: NAD+
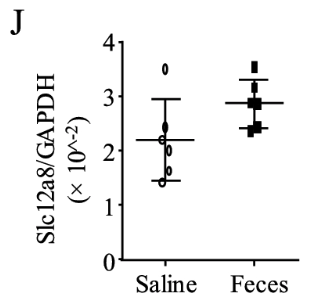
Sepsis-associated disruption of the NRK1/2 pathway for NAD+ synthesis emphasized the critical role of NMN transport through the Slc12a8 transporter.
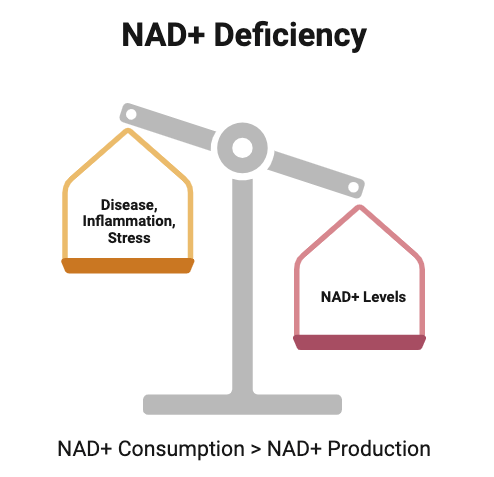
NAD+ deficiency is not just a concern of aging; it also plays a significant role in the development of various chronic diseases that are on the rise among younger generations.
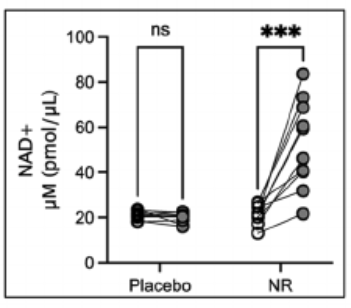
This study showed that NR (1 g/day) for 10 weeks is safe in adults with MCI and effectively increased blood levels of NAD+.
New research on NAD+ metabolism, NMN supplementation, and mitochondrial NAD+ levels was presented at the esteemed longevity conference, the Aging Research and Drug Discovery (ARDD) Meeting.
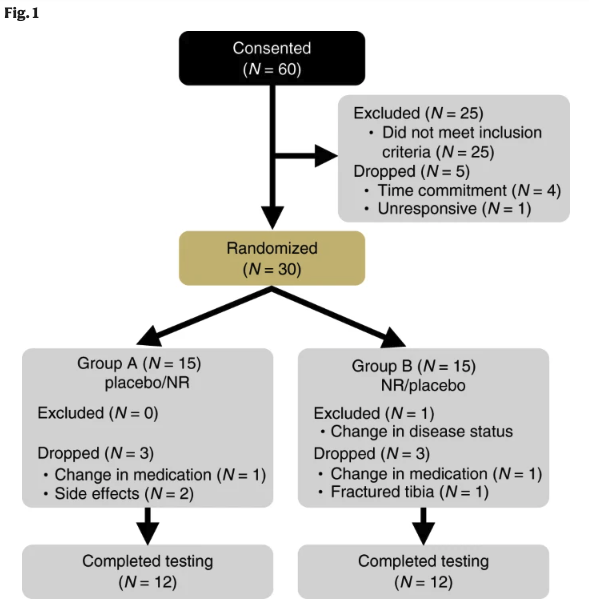
A recent systematic review evaluated ten studies with NAD+ precursors for efficacy and safety.
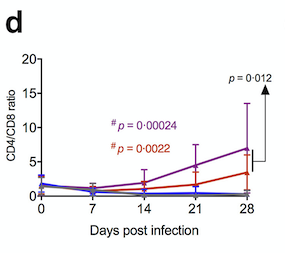
“Results from the humanized mouse study demonstrated that NMN treatment could improve the therapeutic effect of cART in vivo on reconstituting CD4+ T cells and improving CD4/CD8 ratio significantly over time.”
Many diseases and biological stressors disrupt NAD+ metabolism and are associated with low levels of NAD+, such as obesity, infection, alcohol consumption, and high blood pressure.
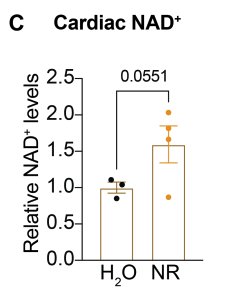
Circadian rhythm is your body’s internal clock that permits anticipation of daily patterns, regulating when it’s time to sleep, wake up, eat, and digest. This study evaluated the effects of NR supplementation on age-related changes in the heart’s circadian rhythm.
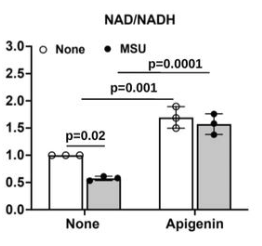
This study evaluated the effects of Apigenin and Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) on factors associated with gouty arthritis.
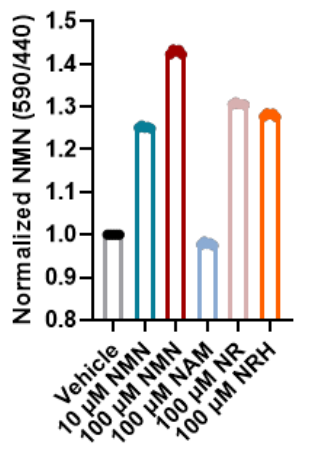
A study reported new insights into NAD+ precursor dynamics using a novel method to follow NMN uptake and metabolism in cells.
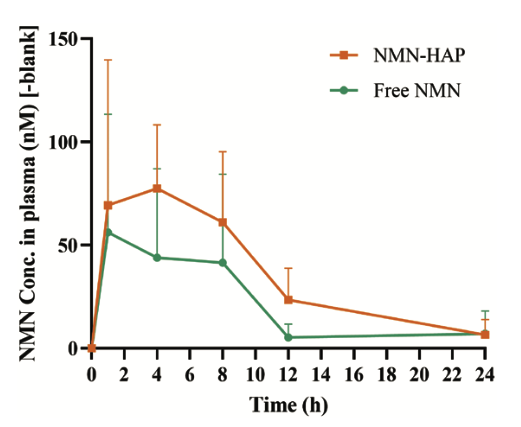
“Upon oral administration, NMN–HAP nanoparticles demonstrated prolonged circulation time and enhanced bioavailability compared with free NMN, leading to elevated plasma levels of both NAD+ and its precursor, NR.”